Business Email Compromise attacks explained clearly reveal why BEC is one of the most financially damaging phishing attacks today. Unlike mass phishing, BEC attacks are highly targeted and focus on manipulating business processes rather than stealing credentials directly.
BEC phishing attacks exploit trust in email communication, internal hierarchies, and routine financial workflows. By impersonating executives, vendors, or partners, attackers convince employees to transfer money or sensitive information willingly. This article explains what Business Email Compromise attacks are, how BEC phishing works, and why these attacks are so effective.
Quick Navigation
What Are Business Email Compromise Attacks?
Business Email Compromise Definition in Phishing
Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks are phishing attacks where attackers impersonate trusted business identities to manipulate financial or administrative actions.
BEC phishing attacks typically aim to:
-
Redirect payments
-
Request urgent wire transfers
-
Steal sensitive business data
Unlike traditional phishing, BEC attacks often contain no links or malware.
This definition builds on the phishing foundation explained in What Is Phishing? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
How Business Email Compromise Attacks Work
BEC Phishing Attack Process Explained
A typical Business Email Compromise attack follows this process:
-
The attacker gains email visibility or spoofs an address
-
A trusted identity is impersonated
-
A legitimate business request is imitated
-
Urgency or secrecy is emphasized
-
The victim completes the transaction
This flow mirrors early manipulation stages of the Social Engineering Attack Lifecycle: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Common Types of Business Email Compromise Attacks
CEO Fraud Business Email Compromise Attacks
In CEO fraud BEC attacks:
-
Attackers impersonate executives
-
Requests are marked urgent or confidential
-
Employees are pressured to act quickly
This relies heavily on authority-based manipulation discussed in The Role of Trust, Fear, and Urgency in Social Engineering
Vendor Invoice Business Email Compromise Attacks
Vendor-related BEC attacks involve:
-
Fake payment update requests
-
Modified bank account details
-
Familiar vendor language
These attacks succeed because they blend into routine finance operations.
Payroll Diversion Business Email Compromise Attacks
In payroll BEC phishing attacks:
-
Employees are asked to update payroll details
-
Requests appear internal and routine
-
Changes are processed without verification
Why Business Email Compromise Attacks Are So Effective
Why BEC Phishing Bypasses Security Controls
BEC attacks succeed because:
-
Emails appear legitimate
-
No malware is involved
-
Requests match normal workflows
This explains why BEC phishing often outperforms technical attacks, as discussed in Why Social Engineering Attacks Are More Effective Than Malware
Business Email Compromise vs Traditional Phishing Attacks
Differences Between BEC Attacks and Email Phishing
Compared to typical email phishing:
-
BEC attacks are highly targeted
-
BEC messages lack obvious red flags
-
BEC attacks focus on money, not credentials
These differences make BEC harder to detect.
How Business Email Compromise Attacks Bypass Detection
Business Email Compromise and Legitimate User Actions
BEC attacks bypass detection by:
-
Using trusted sender names
-
Avoiding links and attachments
-
Triggering valid approvals
This aligns with how social engineering bypasses defenses, as explained in How Social Engineering Attacks Bypass Technical Security
Business Email Compromise Red Flags Employees Miss
Warning Signs of BEC Phishing Attacks
Common BEC warning signs include:
-
Urgent payment requests
-
Requests for secrecy
-
Changes to payment instructions
-
Slight variations in email addresses
These signals overlap with indicators discussed in Common Social Engineering Red Flags Most Users Miss
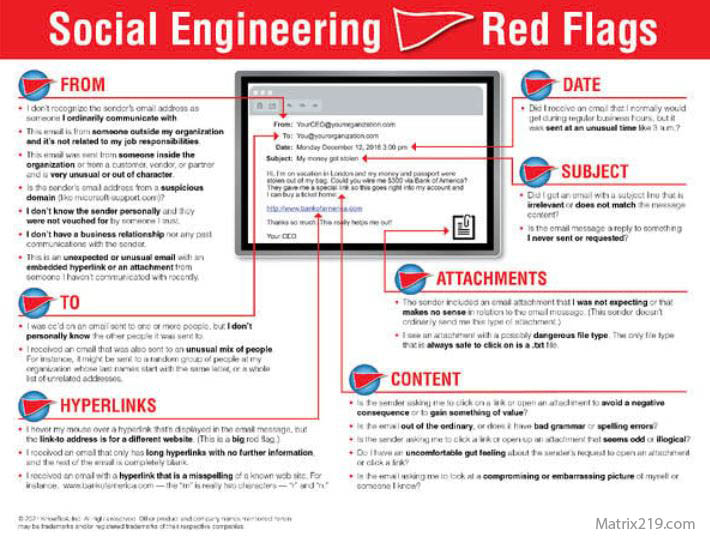
Social Engineering Red Flags
How Organizations Can Prevent Business Email Compromise
Defending Against BEC Phishing Attacks
Effective BEC defenses include:
-
Mandatory payment verification
-
Callback procedures
-
Separation of duties
-
Employee awareness of BEC scenarios
Designing processes that slow down financial actions is critical.
External Perspective on Business Email Compromise Attacks
Cybercrime reports consistently identify Business Email Compromise as one of the costliest phishing threats globally, as highlighted in FBI Business Email Compromise Reports
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Business Email Compromise in simple terms?
BEC is a phishing attack where attackers trick businesses into sending money or sensitive data.
Do BEC attacks use malware?
Often no. Many BEC attacks rely only on email and manipulation.
Are small businesses affected by BEC?
Yes. Small businesses are frequent BEC targets due to limited verification.
Why are BEC attacks hard to detect?
Because they look like normal business emails and requests.
What is the best defense against BEC?
Strong verification for financial and sensitive requests.
Conclusion
Business Email Compromise attacks explained clearly show why BEC is one of the most dangerous forms of phishing. By imitating legitimate business communication and exploiting trust and urgency, attackers bypass security without triggering alarms.
Understanding how BEC phishing works allows organizations to redesign workflows, enforce verification, and prevent small mistakes from becoming costly financial incidents.