In today’s hyperconnected world, organizations are rapidly moving to the cloud to harness scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, with this digital transformation comes an urgent need for robust cloud security solutions. Cybercriminals continuously seek vulnerabilities in cloud environments, and misconfigurations, weak access controls, and compliance gaps often create risks that organizations cannot afford to ignore.
This comprehensive guide explores cloud security solutions in depth, covering their importance, challenges, technologies, strategies, and best practices. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear roadmap for securing your cloud environment while enabling innovation.
Understanding Cloud Security Solutions
What Are Cloud Security Solutions?
Cloud security solutions refer to a set of policies, technologies, applications, and controls designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure hosted in the cloud. They aim to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Why Is Cloud Security Important?
-
Data Protection: Sensitive business and customer data must be shielded against theft or loss.
-
Business Continuity: Cloud downtime or breaches can disrupt operations.
-
Compliance: Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require strict data safeguards.
-
Reputation Management: A single security incident can damage brand trust.
Key Challenges in Cloud Security
Shared Responsibility Model
One of the unique aspects of cloud security is the shared responsibility model.
-
Cloud Providers: Secure the underlying infrastructure (hardware, storage, networking).
-
Customers: Responsible for securing data, user access, and application configurations.
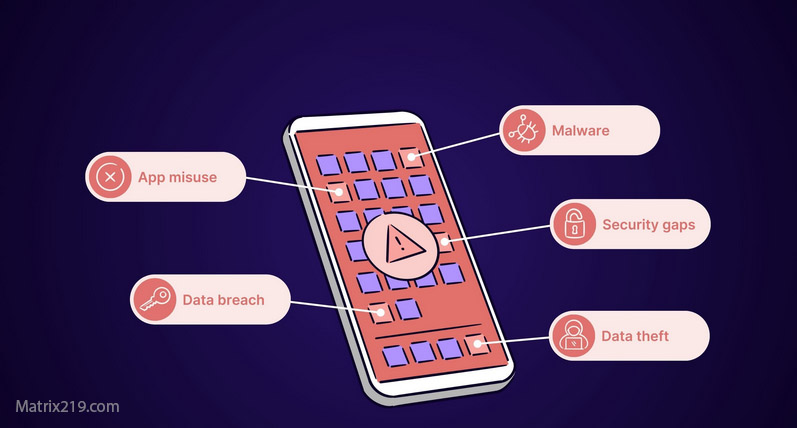
Common Threats to Cloud Security
-
Data Breaches through weak authentication or stolen credentials.
-
Misconfigured Cloud Settings exposing sensitive data.
-
Insider Threats from employees or contractors.
-
Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks targeting cloud servers.
-
Account Hijacking and unauthorized access.
-
Malware Injection into applications and workloads.
Core Cloud Security Solutions
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring multiple verification steps (e.g., password + mobile code).
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Ensures users only have the permissions necessary for their roles, reducing risks of unauthorized access.
Data Encryption
Encryption at Rest
Protects stored data with encryption keys, ensuring that even stolen data remains unreadable.
Encryption in Transit
Secures data moving between cloud services and users through protocols like TLS.
Cloud Firewall and Network Security
Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW)
Provide deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, and traffic filtering.
Secure Network Segmentation
Divides cloud infrastructure into isolated zones to limit attack spread.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM tools continuously monitor cloud configurations for risks, automate compliance checks, and remediate vulnerabilities.
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
CASBs act as a security checkpoint between users and cloud applications.
-
Monitor shadow IT.
-
Enforce policies.
-
Provide threat detection.
Endpoint Security in the Cloud
Secures devices (laptops, smartphones) accessing the cloud with anti-malware, EDR (Endpoint Detection & Response), and device management.
Zero Trust Security Model
The Zero Trust approach assumes no one—inside or outside the network—can be trusted by default.
-
Continuous identity verification.
-
Least-privilege access.
-
Micro-segmentation for workloads.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
CWPP solutions secure workloads across public, private, and hybrid clouds by providing:
-
Runtime protection.
-
Vulnerability scanning.
-
Threat intelligence integration.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) in the Cloud
SIEM systems aggregate logs, detect anomalies, and alert teams in real time, enhancing visibility across cloud platforms.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Major Regulations Affecting Cloud Security
-
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for European data protection.
-
HIPAA for healthcare data privacy.
-
PCI DSS for financial and payment security.
-
ISO/IEC 27017 for cloud-specific security practices.
Achieving Compliance in the Cloud
-
Implement encryption, audit trails, and logging.
-
Regularly conduct risk assessments.
-
Use compliance monitoring tools.

Best Practices for Implementing Cloud Security Solutions
1. Strong Authentication Policies
-
Use MFA for all accounts.
-
Rotate credentials frequently.
2. Data Protection by Design
-
Encrypt sensitive data.
-
Classify and label data properly.
3. Continuous Monitoring
-
Leverage SIEM and CSPM tools.
-
Monitor API traffic for anomalies.
4. Employee Training
-
Educate staff on phishing and insider threats.
-
Provide role-specific training.
5. Regular Penetration Testing
-
Simulate attacks to identify weaknesses.
-
Fix vulnerabilities proactively.
6. Backup and Disaster Recovery
-
Implement automated backups.
-
Test recovery processes regularly.
Emerging Technologies in Cloud Security
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
-
Detect unusual behavior patterns.
-
Automate incident response.
Blockchain in Cloud Security
-
Ensures data integrity.
-
Provides tamper-proof audit trails.
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
-
Combines networking and security in one cloud-based service.
-
Provides scalability and unified protection.
Confidential Computing
-
Protects data while being processed by isolating workloads in secure enclaves.
Cloud Security in Different Environments
Public Cloud Security
-
Strong vendor tools (AWS Shield, Azure Security Center, Google Cloud Security).
-
Extra focus on shared responsibility.
Private Cloud Security
-
Higher control and customization.
-
Requires dedicated security teams.
Hybrid Cloud Security
-
Complex integrations.
-
Unified monitoring tools are critical.
Multi-Cloud Security
-
Consistent policies across multiple vendors.
-
CASBs and CSPMs help manage diverse environments.
Case Studies of Cloud Security Implementation
Financial Services
Banks use IAM, encryption, and SIEM to secure transactions and customer data.
Healthcare
Hospitals deploy HIPAA-compliant CSPM and CWPP tools to safeguard patient records.
E-commerce
Retailers implement CASBs and Zero Trust to protect payment systems and prevent fraud.
The Future of Cloud Security
The next decade will bring more automation, AI-driven detection, decentralized security models, and stronger compliance frameworks. Organizations that adopt proactive and adaptive cloud security solutions will stay ahead of threats while maintaining innovation.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is the backbone of digital transformation, but without robust cloud security solutions, organizations face enormous risks. By implementing IAM, encryption, Zero Trust, CASBs, CWPPs, and SIEM, businesses can protect sensitive data, meet compliance requirements, and ensure operational resilience.
As cloud threats evolve, security strategies must evolve too—embracing AI, blockchain, and SASE. Ultimately, cloud security is not just a technical necessity but a business enabler, empowering organizations to innovate confidently in a digital-first world.