Credential harvesting attacks explained clearly show why stolen usernames and passwords remain one of the most valuable assets for cybercriminals. Rather than breaking systems directly, attackers use phishing attacks to trick users into willingly handing over their login credentials.
Credential harvesting phishing attacks power many larger cyber incidents, including account takeovers, data breaches, and financial fraud. This article explains what credential harvesting attacks are, how credential harvesting phishing works, and why these attacks continue to succeed despite widespread security awareness.
Quick Navigation
What Are Credential Harvesting Attacks in Phishing?
Credential Harvesting Definition in Phishing Attacks
Credential harvesting attacks are phishing attacks designed to steal usernames, passwords, and authentication details from victims.
In credential harvesting phishing attacks, attackers:
-
Create fake login pages
-
Imitate trusted services
-
Capture credentials entered by users
This definition builds directly on the phishing fundamentals explained in What Is Phishing? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
How Credential Harvesting Attacks Work Step by Step
Credential Harvesting Phishing Attack Process Explained
A typical credential harvesting attack follows this flow:
-
A phishing message is delivered
-
A link directs the victim to a fake login page
-
The victim enters credentials
-
Credentials are captured and reused
This process mirrors the early manipulation stages of the Social Engineering Attack Lifecycle: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Common Credential Harvesting Attack Methods
Credential Harvesting via Fake Login Pages
The most common credential harvesting method uses:
-
Cloned websites
-
Lookalike domains
-
Familiar branding
Victims believe they are logging into a real service.
Credential Harvesting Through Email and Messaging Phishing
Credential harvesting attacks are delivered through:
-
Email phishing messages
-
SMS phishing (smishing)
-
Messaging platforms
These delivery methods reflect patterns seen in Email Phishing Examples and How to Spot Them
Why Credential Harvesting Attacks Are So Effective
Why Credential Harvesting Phishing Still Works
Credential harvesting attacks succeed because:
-
Users are accustomed to logging in
-
Fake pages look convincing
-
Urgency pressures quick action
This explains why credential harvesting often outperforms technical attacks, as discussed in Why Social Engineering Attacks Are More Effective Than Malware
Credential Harvesting Attacks vs Malware-Based Credential Theft
Differences Between Credential Harvesting and Malware Attacks
Unlike malware-based theft:
-
Credential harvesting uses no exploits
-
Credential harvesting relies on deception
-
Credential harvesting avoids detection
This makes phishing-based credential theft easier to scale.
How Credential Harvesting Attacks Bypass Security Controls
Credential Harvesting and Legitimate User Behavior
Credential harvesting bypasses security by:
-
Using valid credentials
-
Triggering normal login flows
-
Avoiding malicious software
This aligns with how social engineering bypasses defenses, as explained in How Social Engineering Attacks Bypass Technical Security
What Happens After Credential Harvesting Attacks Succeed
Post-Credential Harvesting Attack Impact
Stolen credentials are used for:
-
Account takeover
-
Lateral movement
-
Financial fraud
-
Data theft
Credential harvesting often acts as the gateway to larger incidents.
Credential Harvesting Red Flags Users Miss
Warning Signs of Credential Harvesting Phishing Attacks
Common red flags include:
-
Unexpected login prompts
-
Slightly altered URLs
-
Requests to re-enter credentials urgently
These indicators overlap with signals covered in Common Social Engineering Red Flags Most Users Miss
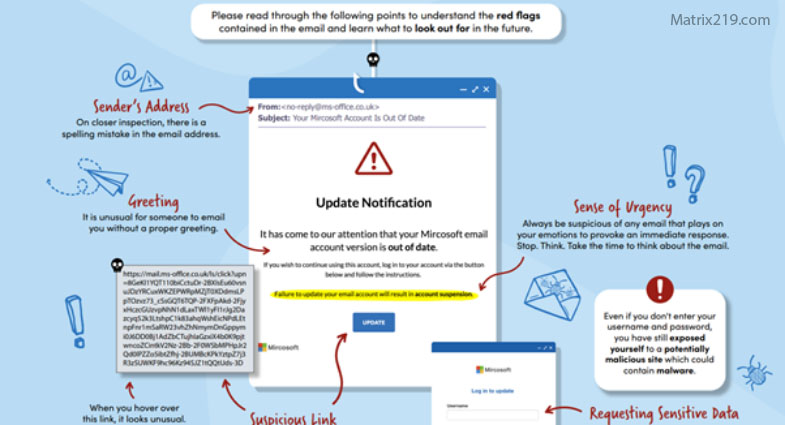
credential harvesting attacks
How to Defend Against Credential Harvesting Attacks
Preventing Credential Harvesting Phishing
Effective defenses include:
-
Verifying URLs before login
-
Using password managers
-
Enabling MFA where possible
-
Educating users about fake login pages
Defense must focus on user interaction, not just tools.
External Perspective on Credential Harvesting Risks
Cybercrime analysis consistently identifies credential harvesting as a primary driver of account compromise, as highlighted in Verizon Credential Theft Analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is credential harvesting in simple terms?
Credential harvesting is tricking users into entering their login details on fake websites.
Are credential harvesting attacks the same as phishing?
Credential harvesting is a common outcome of phishing attacks.
Can MFA stop credential harvesting?
MFA reduces risk but does not prevent credentials from being stolen.
Are fake login pages easy to spot?
Not always. Many are visually identical to real sites.
Why do attackers value stolen credentials?
Because they enable access without triggering security alerts.
Conclusion
Credential harvesting attacks explained in detail show how phishing remains effective by targeting login habits rather than exploiting software. By tricking users into entering credentials on fake pages, attackers gain access that security tools are designed to allow.
Understanding how credential harvesting works helps users pause, verify, and avoid becoming the entry point for larger cyber incidents. In phishing defense, protecting credentials is foundational.