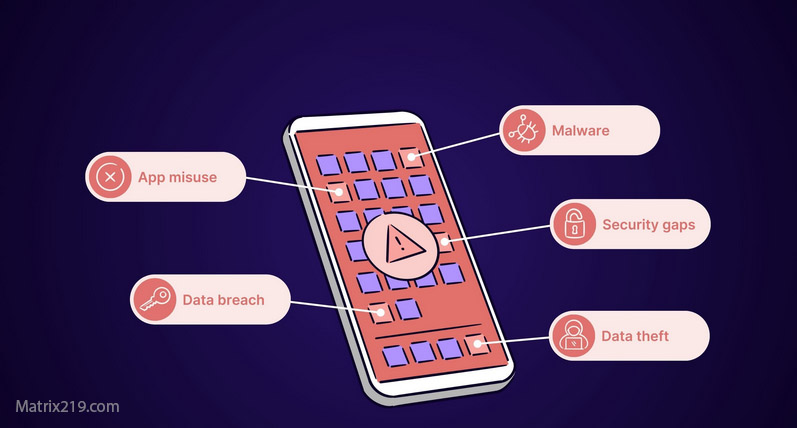
Databases form the backbone of modern information systems, responsible for storing, managing, and processing vast volumes of sensitive and business-critical data. As cyber threats continue to grow in frequency and sophistication, ensuring strong database security has become a fundamental requirement for protecting data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. A successful compromise can lead to data breaches, operational disruption, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage. This article explores essential best practices, modern security technologies, and advanced strategies that organizations can adopt to safeguard their databases against evolving cyber threats.
Importance of Database Security
- Protects Sensitive Data: Shields personal, financial, and medical information from breaches.
- Prevents Financial Losses: Avoids damages from data theft, ransomware, or legal penalties.
- Ensures Regulatory Compliance: Meets strict requirements like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Maintains Business Reputation: Prevents loss of customer trust due to data breaches.
- Ensures Business Continuity: Keeps operations running smoothly despite cyber threats.
- Defends Against Internal and External Threats: Restricts unauthorized access from both cybercriminals and employees.
- Prevents Data Manipulation: Maintains data accuracy and reliability.
- Reduces Operational Costs: Minimizes expenses related to security breaches and damage control.

Key Database Security Technologies
- Encryption:
- Data in Transit: Uses SSL/TLS to protect data during transfer.
- Data at Rest: Encrypts stored data using AES to prevent unauthorized reading.
- Access Control:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Restricts access based on user roles.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of identity verification.
- Password Management:
- Enforces Strong Passwords: Requires complex, hard-to-guess passwords.
- Regular Password Changes: Reduces risk of credential compromise.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS/IPS):
- Auditing and Monitoring:
- Audit Logs: Tracks database activity for security analysis.
- Continuous Monitoring: Detects and alerts against unusual activities.
- Updates and Patch Management:
- Frequent Software Updates: Fixes known vulnerabilities.
- Latest Database Versions: Enhances security features.
- Data Segmentation and Isolation:
- Database Partitioning: Distributes data across multiple servers.
- Sensitive Data Isolation: Keeps critical information separate for added security.
- Backup and Recovery:
- Regular Backups: Ensures data restoration in case of breaches.
- Disaster Recovery Testing: Verifies backup effectiveness.
Best Practices for Database Security
- Regular Security Audits: Identifies vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
- Backup Policies: Ensures quick data recovery after cyber incidents.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Strengthens access security.
- Behavior Monitoring: Detects suspicious activities with log analysis.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls user privileges and data access.

Database Security
Conclusion
Database security is a critical pillar of overall cybersecurity, as databases store some of the most valuable and sensitive information within any organization. By applying industry best practices—such as access control, encryption, regular monitoring, and timely patching—and leveraging advanced security technologies, businesses and individuals can significantly reduce their exposure to cyber threats. A strong database security strategy not only preserves data integrity and availability but also helps ensure compliance with regulatory and legal standards, supporting long-term trust and operational stability.