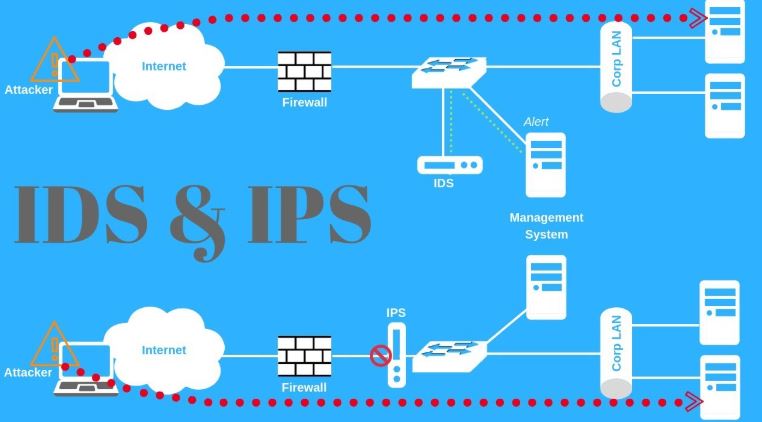
In the world of network security, IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) are essential tools for identifying and stopping cyber threats. While they work closely together, their functions and placement within a network differ significantly.
What Is IDS?
An Intrusion Detection System monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and alerts administrators when potential threats are detected.
-
Function: Detection only (no active blocking).
-
Placement: Often outside the main traffic flow, analyzing mirrored traffic.
-
Example Use Case: Alerting about a potential SQL injection attempt without stopping it.
What Is IPS?
An Intrusion Prevention System not only detects threats but also actively blocks or prevents them from succeeding.
-
Function: Detection and prevention.
-
Placement: Inline with network traffic, enabling real-time blocking.
-
Example Use Case: Detecting and immediately dropping malicious packets from an attacker.
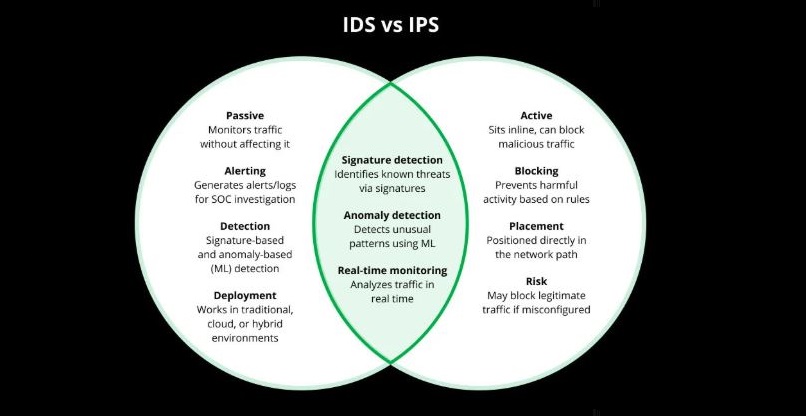
Key Differences Between IDS and IPS
| Feature | IDS (Intrusion Detection System) | IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects threats and alerts | Detects and blocks threats |
| Action | Passive monitoring | Active prevention |
| Placement | Out-of-band | Inline |
| Impact on Traffic | No latency impact | May introduce slight latency |
| Control | Requires admin action | Automatic blocking |
Which Should You Use?
-
IDS is best if you want monitoring without interruption of traffic flow.
-
IPS is ideal when real-time blocking is required to prevent attacks.
-
Many modern systems combine both capabilities into a single Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) or Unified Threat Management (UTM) device.
Key Takeaway
IDS focuses on alerting while IPS focuses on preventing. For comprehensive security, organizations often deploy both, or use integrated solutions that offer the benefits of each.