In today’s connected world, file sharing has become an essential activity for businesses, students, and individuals alike. Whether you are sending sensitive corporate data, personal documents, or academic materials, the way you share files matters. Unfortunately, cybercriminals often target file transfers to intercept confidential data, spread malware, or exploit vulnerabilities.
To ensure privacy, security, and compliance, it’s crucial to adopt the best practices for secure file sharing. This article provides a comprehensive guide on why secure file sharing is important, the risks of unsafe methods, and the most effective tools and techniques to protect your data.
Why Is Secure File Sharing Important?
Protecting Sensitive Information
Files often contain confidential data such as financial records, healthcare information, intellectual property, or personal details. Secure sharing ensures that only authorized individuals can access it.
Preventing Data Breaches
Unauthorized file access can lead to data leaks, financial losses, and reputational harm.
Compliance with Regulations
Laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require organizations to protect sensitive information during transmission and storage.
Maintaining Trust
Employees, customers, and partners expect companies to handle their data responsibly. Secure file sharing builds long-term trust.
Common Risks of Insecure File Sharing
Unencrypted Transfers
Sending files without encryption exposes data to interception during transmission.
Weak Password Protection
Sharing files with easily guessable or reused passwords invites unauthorized access.
Public Cloud Storage Vulnerabilities
Using free or unsecured cloud storage may result in data leaks if accounts are compromised.
Malware and Ransomware Spread
Malicious files can be disguised as legitimate documents and shared without detection.
Phishing Links
Attackers may trick users into downloading files from fake websites or compromised links.

Secure File Sharing Best Practices
1. Use End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
Encryption ensures that files are encrypted on the sender’s device and can only be decrypted by the recipient.
- Tools like Signal, Tresorit, or Proton Drive use strong E2EE.
- Avoid platforms that only encrypt data in transit but not at rest.
2. Choose Trusted File-Sharing Services
Select platforms with zero-knowledge encryption and compliance certifications. Examples include:
- Dropbox Business with advanced security
- OneDrive for Business with Microsoft 365 integration
- Tresorit with full E2EE
3. Password-Protect Shared Files
- Always set strong, unique passwords before sending files.
- Share the password via a different channel (e.g., email the file but send the password via SMS).
4. Enable Expiration Dates and Access Controls
- Set time-limited access to shared files.
- Restrict file downloads or limit access to specific email addresses.
5. Use Secure File Transfer Protocols
- SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
- FTPS (File Transfer Protocol Secure)
- HTTPS-based services for web-based file sharing
6. Avoid Public Wi-Fi When Sharing Files
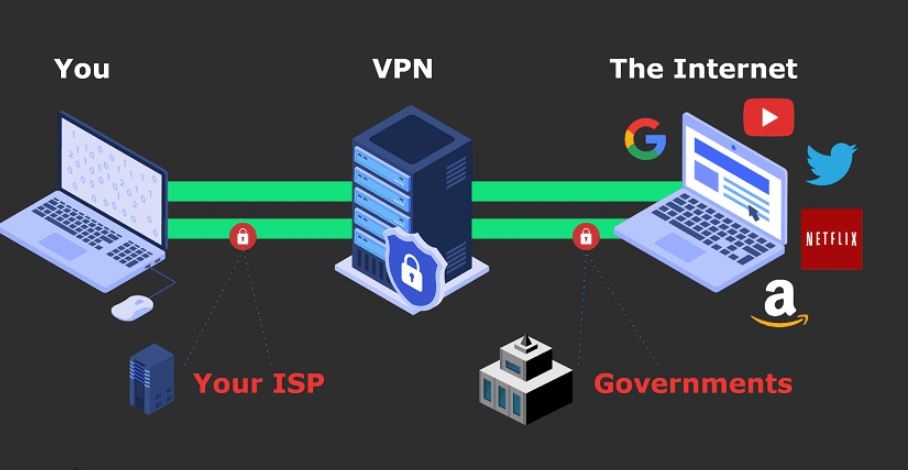
Unsecured networks are prone to man-in-the-middle attacks. Always use a VPN when accessing or sending sensitive files.
7. Keep Software and Devices Updated
Outdated systems may contain vulnerabilities that attackers exploit during file transfers.
8. Scan Files for Malware Before Sharing
Always use antivirus or endpoint protection to ensure files are clean.
9. Educate Users About Phishing Risks
Train employees to recognize suspicious links and verify file-sharing requests.
10. Use Digital Rights Management (DRM)
For highly sensitive business documents, DRM ensures files cannot be copied, printed, or forwarded without permission.

Secure File Sharing in Business Environments
Enterprise File Sync and Share (EFSS)
Solutions like Box, Citrix ShareFile, and Egnyte provide enterprise-level security with:
- Access controls
- User activity monitoring
- Data loss prevention (DLP)
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Businesses should enforce VPN usage for remote employees when accessing shared files.
Data Classification and Policy Enforcement
Organizations must classify data (public, internal, confidential) and apply the appropriate sharing method.
Secure File Sharing for Individuals
Secure Cloud Storage
Individuals can use Google Drive, iCloud, or Dropbox with additional encryption tools like Cryptomator.
Peer-to-Peer Encrypted Sharing
Tools like OnionShare allow users to share files directly over the Tor network.
Secure Messaging Apps
Apps such as Signal and WhatsApp provide encrypted file sharing for small files.
Comparing Secure File-Sharing Methods
| Method | Security Level | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Email with encryption | Medium | Personal files, small businesses |
| Encrypted cloud storage | High | Businesses, long-term storage |
| Secure file transfer (SFTP) | Very High | Large file transfers, enterprise use |
| Peer-to-peer encrypted apps | High | Individuals, privacy-focused users |
| DRM-protected sharing | Very High | Intellectual property, legal documents |
Real-World Examples
Case Study: Dropbox Security Breach (2012)
A stolen password allowed access to user data. Lesson: Always use strong authentication and additional encryption.
Case Study: Healthcare Data Sharing
Hospitals now use HIPAA-compliant platforms for file sharing to avoid massive fines and protect patient data.
Future of Secure File Sharing
AI-Powered Threat Detection
Future platforms will use AI to monitor suspicious activities in shared file links.
Blockchain-Based File Sharing
Blockchain technology may enable decentralized and tamper-proof file transfers.
Quantum-Resistant Encryption
With quantum computing on the rise, stronger encryption algorithms will become standard.
Conclusion
Secure file sharing is not just about convenience—it’s about protecting privacy, complying with laws, and preventing cyber threats. By adopting best practices such as encryption, password protection, access controls, and secure platforms, individuals and businesses can significantly reduce risks.
In an era of increasing cybercrime, knowing how to share files securely is a skill that safeguards both personal and professional digital lives.