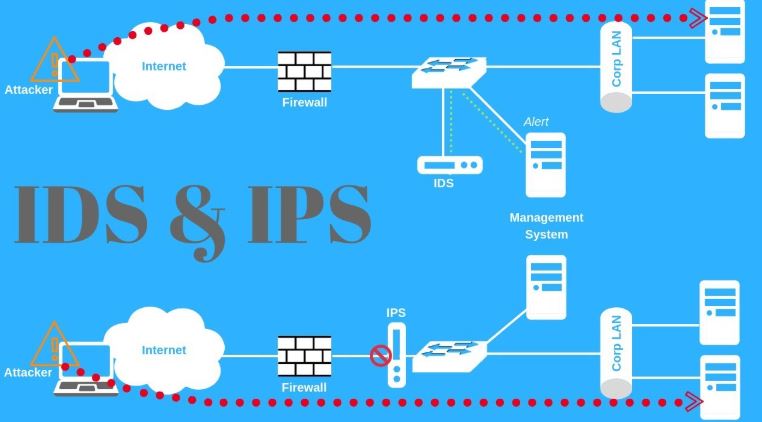
When it comes to protecting a network from cyber threats, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are two critical security tools. While they share similar goals, their roles in defending your infrastructure are distinct.
What Is IDS?
Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a monitoring tool that analyzes network traffic and alerts security teams when suspicious activity is detected.
-
Purpose: Detection only
-
Action: Sends alerts, logs data, and reports anomalies
-
Analogy: Like a security camera that watches but doesn’t intervene
Types of IDS:
-
Network-based IDS (NIDS) – Monitors entire network traffic
-
Host-based IDS (HIDS) – Monitors specific devices or servers

What Is IPS?
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) takes things a step further by actively blocking or preventing malicious traffic in real time.
-
Purpose: Detection + prevention
-
Action: Blocks IP addresses, drops packets, or closes sessions
-
Analogy: Like a security guard who stops the intruder before they enter
Types of IPS:
-
Network-based IPS (NIPS) – Protects entire network segments
-
Host-based IPS (HIPS) – Protects individual devices
IDS vs IPS: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | IDS | IPS |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Detect threats | Detect & prevent threats |
| Response | Passive (alerts only) | Active (blocks attacks) |
| Network Impact | No latency added | May introduce slight latency |
| Placement | Out-of-band monitoring | Inline with traffic flow |
| Example Use Case | Security auditing | Real-time threat blocking |
Which Should You Use?
In practice, many organizations deploy both IDS and IPS as part of an integrated security strategy:
-
IDS is valuable for visibility, compliance, and forensic investigations.
-
IPS is essential for real-time protection against active threats.
Key Takeaway
Think of IDS as the watchdog and IPS as the guard dog. IDS spots suspicious activity, while IPS acts to stop it. For maximum security, using both can give you layered protection.