In today’s digital world, security and privacy are paramount. Decentralized networks like the Matrix Network offer tremendous advantages in communication freedom and data ownership, but securing these networks is equally critical.
Matrix Security refers to the comprehensive set of protocols, practices, and technologies designed to protect the Matrix ecosystem. This includes end-to-end encryption, server authentication, data integrity, federated security measures, and AI-assisted threat detection.
This article explores Matrix Security in depth, covering its architecture, key features, implementation strategies, benefits, challenges, and its role in safeguarding decentralized communication.
What Is Matrix Security?
Definition
Matrix Security encompasses all mechanisms used to protect users, servers, and communications within the Matrix Network, ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and trust in a decentralized environment.
Purpose
The purpose of Matrix Security is to:
-
Protect user messages and files via encryption
-
Secure homeservers and federated servers against attacks
-
Maintain data integrity and authenticity across federated networks
-
Provide privacy-preserving features for users and organizations
Difference Between Matrix Security and General Cybersecurity
-
General cybersecurity focuses on central networks or enterprise systems.
-
Matrix Security specifically addresses decentralized, federated networks where multiple independent servers interact.
Core Components of Matrix Security
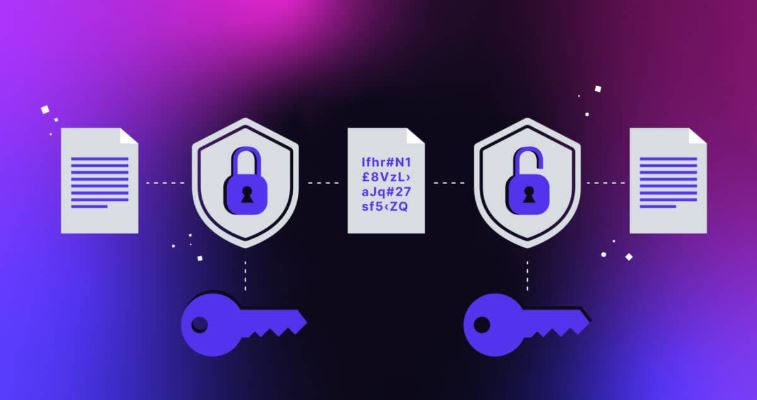
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
-
Uses Olm and Megolm protocols
-
Encrypts messages and files between sender and recipient
-
Ensures server administrators cannot read message content
Server Authentication
-
Homeservers and federated servers authenticate using TLS certificates and signed keys
-
Prevents man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks
Data Integrity
-
All events and messages are cryptographically signed
-
Clients can verify authenticity using event signatures
Access Control and Permissions
-
Granular permissions for rooms, messages, and files
-
Admins can manage who can read, write, or manage rooms
AI-Assisted Security
-
AI modules can detect spam, phishing, or abnormal behavior
-
Provides proactive threat alerts and automated moderation
Blockchain Verification
-
Matrix Blockchain can store immutable records of events and transactions
-
Ensures tamper-proof verification for sensitive communications
How Matrix Security Works
Encryption Flow
-
User sends a message from a Matrix client (Element, FluffyChat, etc.)
-
The message is encrypted with the recipient’s public key (Olm/Megolm)
-
Encrypted message is transmitted to the homeserver
-
Homeserver federates the encrypted message to other servers if needed
-
Recipient decrypts the message locally
Server-to-Server Security
-
Uses signed JSON and TLS for authentication and secure communication
-
Ensures messages and state updates cannot be tampered with during federation
Key Management
-
Each device generates unique encryption keys
-
Users verify devices via QR codes or cryptographic fingerprints
-
Keys can be backed up and restored securely
Monitoring and Threat Detection
-
AI and analytics monitor unusual login patterns, brute-force attempts, and potential exploits
-
Alerts administrators and triggers automated mitigation
Key Features of Matrix Security
Privacy Protection
-
E2EE ensures only intended recipients can access content
-
Users maintain control over their data
Federated Security
-
Each server manages its own security policies
-
Federation protocols ensure secure cross-server communication
Tamper-Proof Records
-
Cryptographic signatures and optional blockchain anchoring ensure data integrity
Access Management
-
Role-based permissions in rooms and channels
-
Fine-grained control over who can read, write, or manage content
AI Security
-
Detects spam, phishing, abuse, or malicious activity
-
Automates moderation while respecting privacy
Compliance Support
-
Matrix Security allows organizations to implement privacy and regulatory compliance measures, including GDPR and HIPAA
Advantages of Matrix Security
Enhanced Privacy
-
Users’ messages and files remain confidential
-
Encryption ensures protection against unauthorized access
Decentralized Protection
-
No single point of failure
-
Federated servers share responsibility for security
Integrity and Trust
-
Cryptographic verification ensures messages and events are authentic
-
Blockchain integration adds tamper-proof verification
Automation and Intelligence
-
AI modules detect threats in real time
-
Reduces workload for server administrators and moderators
Flexibility
-
Security measures can be customized for each server, room, or organization
-
Supports diverse use cases from personal messaging to enterprise collaboration
Challenges and Limitations
Key Management Complexity
-
Users must verify devices and manage backups carefully
-
Mismanagement may result in lost encrypted data
Federated Trust
-
Trusting external servers in federation requires careful configuration
-
Rogue servers could attempt attacks on the federation
Performance Considerations
-
Encryption, AI monitoring, and blockchain anchoring consume server and client resources
Adoption and Awareness
-
Users and organizations must understand best practices for maximum security benefits
Real-World Applications
Personal Messaging
-
Secure, private chats without dependence on centralized platforms
Enterprise Collaboration
-
Confidential communications and file sharing
-
Audit logs and access controls for compliance
Government Communications
-
Secure messaging for officials and public sector organizations
-
Tamper-proof verification of messages and records
Activist Networks
-
Censorship-resistant, private communication channels
-
AI-assisted moderation and threat detection
IoT and Smart Devices
-
Secure device communication using Matrix protocols
-
Encryption and verification for federated IoT networks

Matrix Security and the Matrix Ecosystem
Element Client Integration
-
E2EE and key verification built into the client
-
AI modules operate without compromising encryption
Developer Opportunities
-
Create secure bots, analytics, and dApps
-
Integrate blockchain verification for critical events
Federation and Interoperability
-
Security protocols apply across federated servers
-
Bridges to external platforms respect encryption and access controls
Future of Matrix Security
Advanced AI Threat Detection
-
Predictive AI models to detect suspicious activity and security breaches
Quantum-Resistant Encryption
-
Preparing Matrix ecosystem for post-quantum security
Wider Federation Security
-
Standardized security protocols across all Matrix servers
-
Easier verification and trust management
Compliance and Privacy Enhancements
-
Enhanced privacy features for regulatory compliance
-
User-centric data ownership and control
Secure Decentralized Applications
-
Matrix Security ensures dApps can operate securely and trustlessly
-
Blockchain anchoring for critical actions and transactions
Conclusion
Matrix Security is the cornerstone of safe and reliable communication within the Matrix Network. By integrating end-to-end encryption, federated security, AI-assisted threat detection, and blockchain verification, it ensures privacy, data integrity, and trust in decentralized environments.
Whether for personal messaging, enterprise collaboration, government communication, or activist networks, Matrix Security provides the tools and protocols necessary to maintain a secure, private, and tamper-proof decentralized communication ecosystem.
While challenges like key management and federated trust remain, the continuous development of Matrix Security positions it as a robust foundation for the future of secure digital communication.