How phishing bypasses multi-factor authentication is one of the most misunderstood topics in modern cybersecurity. Many users believe that enabling MFA makes accounts “unhackable.” In reality, phishing attacks have evolved specifically to work around MFA protections.
Phishing does not always break MFA technically—it often bypasses it by manipulating users into approving access or handing over valid session data. This article explains how phishing bypasses multi-factor authentication, which MFA phishing techniques attackers use, and why MFA alone is not a complete defense.
Quick Navigation
How Phishing Bypasses Multi-Factor Authentication in Practice
How MFA Phishing Attacks Exploit Human Approval
Most MFA systems assume users will:
-
Recognize legitimate login attempts
-
Deny suspicious approval requests
-
Verify context before approving
Phishing attacks exploit this assumption by creating believable login scenarios that convince users to approve access voluntarily.
This weakness ties directly to concepts explained in Why Humans Are the Weakest Link in Cybersecurity
MFA Fatigue Phishing Attacks Explained
How MFA Fatigue Phishing Bypasses Authentication
MFA fatigue phishing attacks work by:
-
Sending repeated MFA push requests
-
Creating annoyance and urgency
-
Pressuring users to approve just to stop alerts
Once approved, attackers gain full access without needing passwords.
This technique fits within the manipulation stages of the Social Engineering Attack Lifecycle: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Real-Time Phishing Proxies and MFA Bypass
How Phishing Proxies Bypass MFA in Real Time
Advanced phishing attacks use:
-
Real-time phishing proxy tools
-
Legitimate login pages
-
Session interception
When a victim logs in and completes MFA, the attacker captures the authenticated session instantly.
This technique is commonly used in Credential Harvesting Attacks Explained
OAuth Phishing and MFA Bypass
How OAuth Phishing Bypasses Multi-Factor Authentication
OAuth phishing bypasses MFA by:
-
Requesting app permissions instead of passwords
-
Using legitimate authorization flows
-
Maintaining persistent access
Because MFA protects logins—not permissions—OAuth phishing succeeds silently, as detailed in OAuth Phishing: The New Silent Account Takeover
SMS and Voice-Based MFA Phishing Attacks
How Smishing and Vishing Bypass MFA
Attackers use:
-
SMS phishing to steal one-time codes
-
Voice phishing to trick users into sharing MFA tokens
These attacks rely on urgency and authority, techniques explained in The Role of Trust, Fear, and Urgency in Social Engineering
Why MFA Alone Cannot Stop Phishing Attacks
Limits of Multi-Factor Authentication Against Phishing
MFA fails against phishing when:
-
Users approve malicious requests
-
Sessions are hijacked after login
-
Attackers exploit trusted workflows
This explains why phishing often outperforms technical controls, as discussed in Why Social Engineering Attacks Are More Effective Than Malware
How Phishing Bypasses MFA Without Malware
MFA Bypass Through Legitimate Actions
Many MFA bypass attacks:
-
Use no malware
-
Trigger valid authentication
-
Leave minimal forensic traces
This aligns with how social engineering bypasses technical defenses, as explained in How Social Engineering Attacks Bypass Technical Security
Red Flags That Indicate MFA Phishing Attacks
Warning Signs of MFA Phishing
Common MFA phishing indicators include:
-
Unexpected MFA prompts
-
Repeated push notifications
-
Login requests from unusual times or locations
These signs overlap with broader warning patterns covered in Common Social Engineering Red Flags Most Users Miss
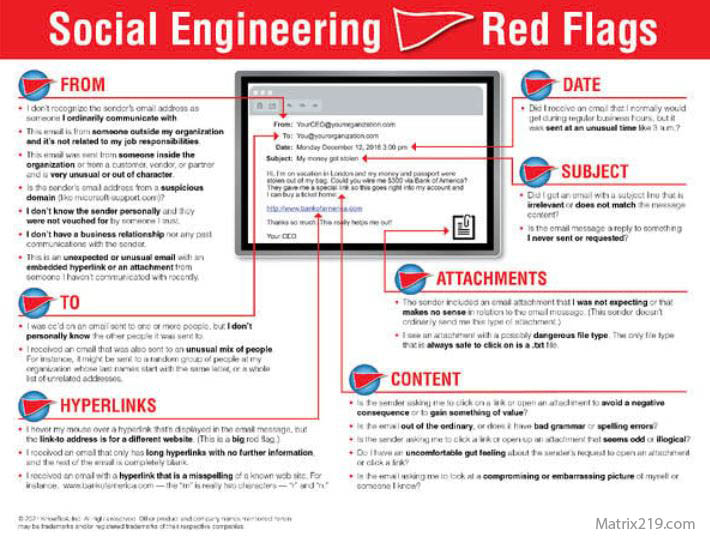
Social Engineering Red Flags
How Organizations Can Reduce MFA Phishing Risk
Defending Against MFA Bypass Phishing Attacks
Effective defenses include:
-
Number-matching MFA
-
Context-aware authentication
-
Limiting push-based approvals
-
Educating users about MFA abuse
MFA must be paired with behavior-aware controls.
External Perspective on MFA Phishing Risks
Security frameworks increasingly warn that MFA does not eliminate phishing risk and must be implemented with user-aware safeguards, a reality emphasized in Microsoft MFA Security Guidance
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can phishing really bypass MFA?
Yes. Phishing often bypasses MFA by tricking users into approving access.
Is MFA still worth using if phishing bypasses it?
Yes. MFA reduces risk significantly but is not a standalone solution.
Which MFA methods are most vulnerable to phishing?
Push notifications and SMS-based MFA are the most abused.
Does hardware-based MFA stop phishing?
It reduces risk but does not eliminate user manipulation entirely.
What is the best defense against MFA phishing?
Combining MFA with context checks, user education, and verification policies.
Conclusion
How phishing bypasses multi-factor authentication highlights a critical truth: security controls that rely on perfect human judgment will always be vulnerable. Phishing attacks succeed by manipulating trust, urgency, and routine—not by breaking encryption.
MFA remains essential, but it must be implemented with awareness of how phishing adapts. In modern phishing defense, authentication must account for human behavior as much as technical strength.





