How attackers clone legitimate websites for phishing explains why phishing websites often look indistinguishable from real services. Website cloning for phishing allows attackers to steal credentials, session data, and approvals without triggering technical alarms.
Phishing websites succeed because users trust familiar layouts, logos, and URLs. By cloning legitimate websites, attackers remove doubt and speed up victim compliance. This article explains how phishing website cloning works, the techniques attackers use, and how users can recognize cloned phishing websites before damage occurs.
Quick Navigation
What Is Website Cloning for Phishing Attacks?
Website Cloning for Phishing Definition Explained
Website cloning for phishing is a technique where attackers create a near-identical copy of a legitimate website to trick users into entering sensitive information.
Phishing website clones typically:
-
Replicate logos and branding
-
Copy page layouts and text
-
Mimic login and consent flows
This technique builds on phishing fundamentals explained in What Is Phishing? A Complete Beginner’s Guide
How Phishing Website Cloning Works Step by Step
Phishing Website Cloning Attack Process Explained
A typical phishing website cloning attack follows this sequence:
-
A target website is selected
-
Page content is copied or mirrored
-
A lookalike domain is registered
-
Victims are redirected to the cloned phishing website
This process mirrors early manipulation stages of the Social Engineering Attack Lifecycle: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Common Techniques Used in Phishing Website Cloning
HTML Copying Techniques in Phishing Websites
Attackers often:
-
Copy HTML and CSS directly
-
Mirror entire websites
-
Modify forms to capture credentials
These cloned phishing websites load quickly and appear authentic.
Lookalike Domains in Phishing Website Cloning
Phishing website cloning relies on:
-
Typosquatting domains
-
Subdomain tricks
-
International character substitutions
These domain tricks are subtle and often missed during quick checks.
Phishing Websites That Clone Login Pages
Login Page Phishing Website Cloning Explained
The most common phishing website clones target:
-
Email login pages
-
Cloud services
-
Banking portals
Victims believe they are signing in normally and submit credentials willingly, enabling Credential Harvesting Attacks Explained
Phishing Website Cloning and MFA Bypass
How Cloned Phishing Websites Bypass MFA
Advanced phishing websites:
-
Relay credentials in real time
-
Proxy MFA challenges
-
Capture authenticated sessions
This explains how phishing websites bypass MFA protections, as discussed in How Phishing Bypasses Multi-Factor Authentication
Why Phishing Website Clones Are Hard to Detect
Why Cloned Phishing Websites Look Legitimate
Phishing website clones are difficult to detect because:
-
Visual design is accurate
-
HTTPS certificates are valid
-
URLs look convincing
These factors create false confidence and reduce verification.
How Phishing Website Cloning Bypasses Security Controls
Phishing Website Cloning vs Technical Security
Phishing website cloning bypasses security by:
-
Using legitimate-looking pages
-
Avoiding malware
-
Triggering valid user actions
This aligns with how social engineering bypasses defenses, as explained in How Social Engineering Attacks Bypass Technical Security
Phishing Website Cloning Red Flags Users Miss
Warning Signs of Phishing Website Clones
Common phishing website clone indicators include:
-
Slightly altered URLs
-
Unexpected login prompts
-
Requests to re-authenticate urgently
These warning signs overlap with patterns discussed in Common Social Engineering Red Flags Most Users Miss
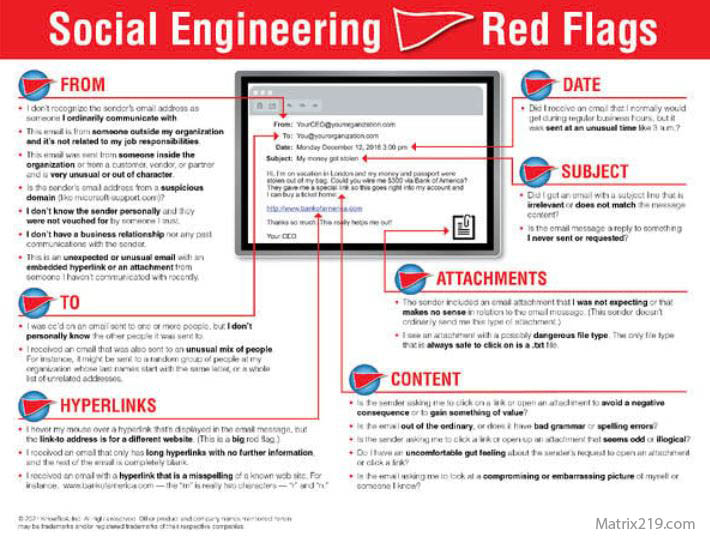
Social Engineering Red Flags
How to Defend Against Phishing Website Cloning
Preventing Phishing Website Clone Attacks
Effective defenses include:
-
Checking URLs carefully before login
-
Using password managers to validate domains
-
Avoiding login links in messages
-
Educating users about cloned phishing websites
Defense depends on slowing down interaction.
External Perspective on Phishing Website Cloning
Security research consistently warns that website cloning is a primary driver of credential theft, as highlighted in Google Safe Browsing Phishing Guidance
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is phishing website cloning in simple terms?
It is copying a real website to trick users into entering credentials on a fake page.
Are cloned phishing websites visually identical?
Often yes. Visual similarity is intentional to remove suspicion.
Can HTTPS prevent phishing website cloning?
No. HTTPS only encrypts traffic and does not verify legitimacy.
Do phishing websites always steal passwords?
Mostly, but some capture sessions or authorization tokens instead.
Who is most at risk from phishing website cloning?
Users who log in through links in emails or messages.
Conclusion
How attackers clone legitimate websites for phishing shows why phishing websites remain one of the most effective attack tools. By copying trusted designs and workflows, attackers remove friction and manipulate users into handing over access willingly.
Recognizing phishing website cloning techniques helps users pause, verify URLs, and avoid interacting with fake pages. In phishing defense, knowing how clones are built is key to spotting them early.