What Is WPA3 Encryption?
WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3) is the most recent standard for securing Wi-Fi connections, introduced by the Wi-Fi Alliance in 2018. It replaces WPA2, which had been the standard since 2004. WPA3 aims to fix vulnerabilities in older protocols, making it harder for hackers to break into wireless networks and steal sensitive data.
Why Was WPA3 Developed?
WPA2, while widely used, had weaknesses such as the KRACK (Key Reinstallation Attack) vulnerability discovered in 2017. These flaws showed that stronger encryption and authentication methods were needed. WPA3 was developed to provide robust protection against brute-force attacks, improve privacy on public networks, and strengthen Wi-Fi security for the growing number of connected devices.
Key Features of WPA3 Encryption
Stronger Password Protection
-
Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) replaces WPA2’s Pre-Shared Key (PSK) system.
-
Even if a password is weak, WPA3 makes it much harder for hackers to guess it using brute-force methods.
Forward Secrecy
-
Ensures that even if a password is compromised in the future, past communications remain secure.
Individualized Data Encryption
-
In open Wi-Fi networks (like coffee shops or airports), WPA3 encrypts traffic between each device and the router.
-
This prevents eavesdropping by other users on the same public hotspot.
Protection Against Offline Attacks
-
WPA3 prevents attackers from capturing encrypted data and then attempting to crack the password offline.
Easy Connect for IoT Devices
-
WPA3 supports “Wi-Fi Easy Connect,” making it simpler to securely connect smart devices that lack displays.
WPA3 vs. WPA2: What’s the Difference?
WPA2
-
Uses Pre-Shared Key (PSK) authentication.
-
Vulnerable to brute-force and dictionary attacks.
-
Still widely used but considered less secure.
WPA3
-
Uses SAE for stronger, more secure authentication.
-
Offers better protection in public Wi-Fi environments.
-
Provides encryption even on open networks.
-
Designed to handle the rise of IoT and smart devices.
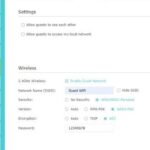
How to Enable WPA3 on Your Router
Step 1: Check Router Compatibility
Not all routers support WPA3. Verify in your router’s specifications or admin settings.
Step 2: Update Router Firmware
Manufacturers often release updates to enable WPA3 support.
Step 3: Change Wi-Fi Security Settings
-
Log into your router’s admin panel.
-
Navigate to Wireless Settings > Security Mode.
-
Select WPA3 or WPA3/WPA2 mixed mode for compatibility.
Step 4: Reconnect Devices
Some older devices may not support WPA3. Use mixed mode if needed.
Benefits of Using WPA3
-
Improved Security: Stronger defense against hacking attempts.
-
Better Privacy: Individualized encryption for public Wi-Fi.
-
Future-Proofing: Designed to secure the growing number of smart devices.
-
Peace of Mind: Even weak passwords are better protected compared to WPA2.
Limitations of WPA3
-
Device Compatibility: Older smartphones, laptops, or IoT devices may not support WPA3.
-
Router Upgrade Needed: Some users may need to buy a new router to enable WPA3.
-
Adoption in Progress: Not all networks or public hotspots have migrated to WPA3 yet.
Conclusion: The Future of Wi-Fi Security
Understanding what WPA3 encryption is helps users recognize the importance of upgrading network security. With stronger authentication, forward secrecy, and improved protection on public Wi-Fi, WPA3 is a major step forward from WPA2. While adoption is still growing, enabling WPA3 where possible ensures your home and public connections are far more secure against modern cyber threats.