Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid
Quick Navigation
Introduction
File encryption is often treated as a “set it and forget it” security measure. In reality, most encryption failures happen not because encryption is weak, but because it is used incorrectly. In 2026, Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid is a high-trust topic because real-world data loss and breaches are overwhelmingly caused by human and operational errors—not broken algorithms.
This article breaks down the most frequent and dangerous mistakes people make when encrypting files. Each mistake is explained in practical terms, with a focus on why it happens, what the real consequences are, and how to avoid it. Understanding these pitfalls is essential if you want encryption to protect your data instead of becoming a false sense of security.
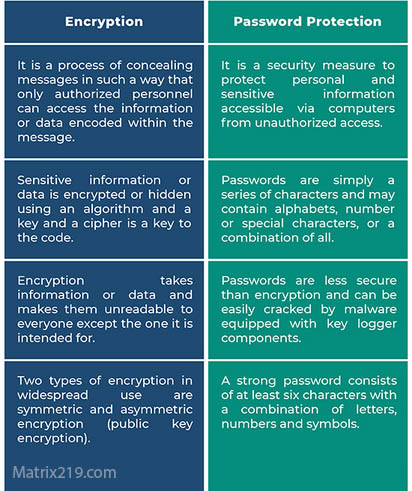
Mistake 1: Confusing Password Protection With Encryption
Why This Happens
Many tools label weak file locks as “encryption,” misleading users.
Why It’s Dangerous
Password-protected files using legacy methods can often be bypassed or cracked.
How to Avoid It
Use true file encryption that transforms the entire file into unreadable data.
This confusion is explained in depth in Encryption vs Password Protection.
Mistake 2: Storing Encryption Keys With Encrypted Files
Why This Happens
Users prioritize convenience over security.
Why It’s Dangerous
If attackers access both the file and the key, encryption provides zero protection.
How to Avoid It
Store keys separately—preferably offline or in a secure key manager.
This is one of the most common real-world failures.
Mistake 3: Losing Encryption Keys Without Backup
Why This Happens
Users underestimate how unforgiving encryption is.
Why It’s Dangerous
Lost keys usually mean permanent data loss.
How to Avoid It
Back up keys securely and test recovery before relying on encryption.
Key-loss consequences are explained in What Happens If You Lose an Encryption Key?
Mistake 4: Encrypting Files on Compromised Devices
Why This Happens
Users assume encryption protects against malware automatically.
Why It’s Dangerous
Malware can capture keys or plaintext during encryption or decryption.
How to Avoid It
Ensure devices are clean and trusted before encrypting sensitive files.
This limitation is explored in Is File Encryption Really Secure?.
Mistake 5: Leaving Plaintext Copies Behind
Why This Happens
Temporary files, backups, or “original” versions are forgotten.
Why It’s Dangerous
Unencrypted copies negate the value of encryption.
How to Avoid It
Verify that originals, temp files, and cache copies are removed securely.
This mistake appears frequently in audits and investigations.
Mistake 6: Using Weak or Reused Passwords as Keys
Why This Happens
Humans are bad at generating strong secrets.
Why It’s Dangerous
Weak passwords can still be brute-forced despite strong algorithms.
How to Avoid It
Use long, unique keys or passphrases generated securely.
Password risks are tied to Encryption vs Password Protection.
Encryption vs Password Protection
Mistake 7: Encrypting Everything Without a Strategy
Why This Happens
Users try to “be safe” without planning.
Why It’s Dangerous
Over-encryption creates performance issues and key management chaos.
How to Avoid It
Encrypt high-risk files first and define clear policies.
Strategic planning is discussed in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide).
Mistake 8: Assuming Cloud Storage Encryption Is Enough
Why This Happens
Cloud providers advertise strong security by default.
Why It’s Dangerous
Provider-controlled keys may still allow access under certain conditions.
How to Avoid It
Use client-side encryption for sensitive files before upload.
Cloud risks are explained in File Encryption for Cloud Storage.
Mistake 9: Failing to Revoke Access and Rotate Keys
Why This Happens
Key lifecycle management is often ignored.
Why It’s Dangerous
Former users may retain access indefinitely.
How to Avoid It
Rotate keys and revoke access when roles or devices change.
Business impact is discussed in File Encryption Software for Business.
Mistake 10: Trusting Fake or Misleading Encryption Tools
Why This Happens
Marketing claims are easier to understand than technical reality.
Why It’s Dangerous
Some tools only obfuscate files rather than encrypting them.
How to Avoid It
Verify documentation, standards, and independent validation.
Red flags are explained in Signs Your File Encryption Software Is Fake.
Why These Mistakes Matter More Than Algorithms
Encryption Rarely Fails Mathematically
Most failures occur before or after encryption.
Human Behavior Is the Weakest Link
Convenience-driven decisions undermine security.
Process Matters More Than Tools
Good encryption requires discipline and planning.
This reality shapes modern security guidance.
How to Build Safer Encryption Habits
Treat Keys as Critical Assets
Protect them more carefully than the files themselves.
Minimize Plaintext Exposure
Decrypt only when necessary and for short periods.
Test Your Assumptions
Verify backups, recovery, and access regularly.
A full best-practice framework is provided in Best File Encryption Software Compared (2026).
Standards and Security Reality
Security guidance aligned with NIST encryption standards assumes that user error—not weak cryptography—is the primary cause of encryption failure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the most common encryption mistake?
Storing keys with encrypted files or losing keys entirely.
Is over-encryption a real problem?
Yes. It increases complexity and failure risk without proportional benefit.
Are free encryption tools more prone to mistakes?
Not inherently—but they place more responsibility on the user.
Can encryption mistakes be reversed?
Sometimes, but many mistakes result in permanent data loss.
Is encryption still worth using despite these risks?
Yes. When used correctly, encryption is one of the strongest protections available.





