Image files often contain more sensitive information than users realize. Personal photos, scanned IDs, medical images, design assets, and screenshots can expose identities, locations, and confidential data if accessed without permission. In 2026, How to Encrypt Image Files Securely is a growing concern because images are shared constantly across messaging apps, cloud storage, and external devices—often without proper protection.
This article explains how image file encryption actually works, why common “image locking” methods fail, and how to protect image files without degrading quality or breaking accessibility. The focus is on real security behavior rather than visual tricks, helping you avoid weak protection methods that only appear secure.
Quick Navigation
Why Image Files Require Proper Encryption
Images Often Contain Hidden Sensitive Data
Metadata such as location, device details, and timestamps can reveal more than the image itself.
Images Are Frequently Shared
Photos are commonly sent through email, messaging apps, and cloud links, increasing exposure.
Visual Files Are Easy to Copy
Once accessed, images can be duplicated instantly without trace.
This risk profile makes images a prime candidate for file-level encryption.
Image Encryption vs Image Hiding Techniques
Visual Obfuscation Is Not Encryption
Blurring, watermarking, or hiding files does not prevent access to original data.
Password-Protected Archives vs File Encryption
Archiving images with weak password protection offers limited resistance.
True Image File Encryption
Encryption transforms the entire image file into unreadable data until decrypted.
A foundational comparison is explained in Encryption vs Password Protection
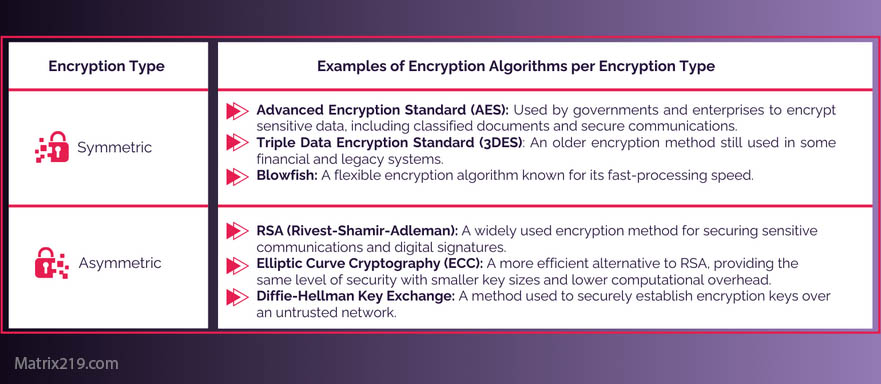
How Image File Encryption Works
Encrypting the Entire File Binary
Secure tools encrypt the full image data, not just visible pixels.
Preserving Image Quality
Proper encryption does not alter resolution, compression, or color data.
Controlled Decryption
Only authorized users with valid keys can restore the original image.
A process overview is covered in How File Encryption Works (Beginner Friendly).
Common Risks When Encrypting Image Files
Metadata Leakage
Some tools encrypt the image but leave metadata exposed.
Temporary Plaintext Previews
Preview generation can create unencrypted cached copies.
Incompatible Formats
Encrypted images may not preview correctly without proper software.
These issues are frequently discussed in Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid
Encrypting Images for Personal Use
Protecting Private Photos
Encryption prevents unauthorized access if devices are lost or compromised.
Secure Backup of Image Archives
Encrypted backups reduce exposure during storage and transfer.
Sharing Images Selectively
Encryption allows controlled access without permanently exposing images.
Personal protection scenarios are grounded in Is File Encryption Really Secure?
Encrypting Images for Professional and Business Use
Design and Creative Assets
Encrypted images protect intellectual property during collaboration.
Medical and Identity Images
Strong encryption is essential for compliance and confidentiality.
Legal and Financial Image Records
Scanned documents require the same protection as original files.
Professional workflows are discussed in File Encryption for Legal and Financial Documents
File Encryption for Legal and Financial Documents
Image Encryption and Cloud Storage
Encrypt Before Uploading Images
Client-side encryption ensures cloud platforms cannot view image contents.
Avoid Relying on Gallery-Level Security
Cloud image viewers often bypass local protections.
Syncing Across Devices
Keys must be securely available only to authorized devices.
Cloud-specific risks are explained in File Encryption for Cloud Storage
Performance and Usability Considerations
Large Image Collections
Batch encryption must be efficient to avoid long processing times.
Thumbnails and Indexing
Encrypted images cannot be indexed without decryption.
Avoiding Duplicate Plaintext Copies
Poor workflows often leave unencrypted originals behind.
Performance trade-offs are discussed in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide)
When Image-Specific Encryption Is Not Enough
Mixed File Sets
If images are stored with other sensitive files, broader file encryption may be better.
Long-Term Archives
Key management becomes critical for image libraries stored for years.
Team-Based Image Access
Centralized encryption may be required.
Enterprise scenarios are covered in Centralized File Encryption Management Systems.
Standards and Best Practices for Image Encryption
Reliable image encryption relies on cryptographic methods aligned with NIST encryption standards rather than format-specific or visual protection techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Does encrypting an image reduce its quality?
No. Encryption does not change image resolution or compression.
Can encrypted images be previewed?
Not without decryption. Previews require temporary access.
Is hiding images the same as encrypting them?
No. Hiding does not prevent data access.
Should images be encrypted before cloud upload?
Yes. Client-side encryption offers the strongest protection.
Are encrypted images safe for long-term storage?
Yes, if encryption keys are stored and backed up properly.





