Many users assume that adding a password to a file provides the same level of security as encryption, but this assumption often leads to serious data exposure. Encryption vs Password Protection is a critical comparison in 2026 because files are no longer stored or shared in isolated environments. Documents are emailed, uploaded to cloud platforms, synced across devices, and moved using external drives.
This article explains the real difference between encrypting a file and simply protecting it with a password. You will learn how each method works, what threats they can and cannot stop, and why password protection often creates a false sense of security. Understanding this distinction is essential before choosing any file protection tool, especially if you rely on sensitive personal data, business documents, or legally regulated information. The goal here is clarity—not fear—so you can choose the right protection method based on actual risk, not assumptions.
Quick Navigation
What Password Protection Really Does
Application-Level Access Control
Password protection usually restricts access through a specific application, not the file itself. Once bypassed or extracted, the file contents may be exposed.
Passwords Are Often Stored or Verified Insecurely
Many formats rely on weak hashing or legacy mechanisms that can be bypassed with modern tools.
What File Encryption Actually Does
Data-Level Protection
Encryption transforms the file’s contents into unreadable data, regardless of where the file is copied or opened.
Independent of the Application
Even if the file is accessed outside its original software, encrypted data remains protected.
A foundational explanation is available in What Is File Encryption and Decryption?
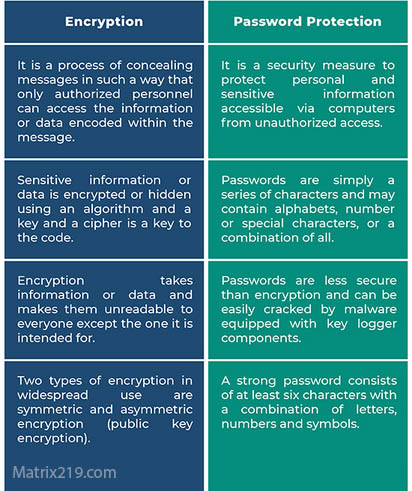
Key Differences Between Encryption and Password Protection
Strength Against Offline Attacks
Encrypted files resist brute-force and offline analysis far better than password-protected files.
Dependency on Software Environment
Password protection often fails once files leave the original application or format.
Key vs Password Security
Encryption relies on cryptographic keys, while password protection often relies on human-memorable secrets.
Encryption vs Password Protection
Real-World Scenarios Where Password Protection Fails
Email Attachments
Password-protected files can often be cracked once intercepted.
Cloud Storage Sharing
If the platform processes the file, password protection may be stripped or bypassed.
Archive and Document Formats
Older formats provide minimal resistance to modern attack tools.
These risks are discussed further in Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid.
When Password Protection Might Still Be Acceptable
Low-Risk, Temporary Files
For short-lived, non-sensitive data, password protection may be sufficient.
Internal Convenience, Not Security
Passwords can deter casual access but should never be treated as strong security.
Why Encryption Is the Preferred Standard
Protection Beyond Device Boundaries
Encrypted files remain secure even when shared, copied, or stolen.
Compliance and Legal Requirements
Many regulations explicitly require encryption rather than simple password protection.
Long-Term Reliability
Encryption scales better as threats evolve.
A broader framework is covered in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide).
How Encryption and Password Protection Are Sometimes Combined
Passwords as Key Accessors
Some tools use passwords to unlock encryption keys, not to protect files directly.
Why This Distinction Matters
The security comes from encryption, not from the password itself.
A technical comparison of key models is explained in Symmetric vs Asymmetric File Encryption.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Files
Ask the Right Questions
-
What happens if the file is copied?
-
Can the protection survive outside the original software?
-
Is compliance required?
Avoid False Security
Choosing password protection instead of encryption often increases risk rather than reducing it.
Use this comparison alongside File Encryption vs Disk Encryption to build a complete protection strategy.
Standards and Best Practices
Modern security recommendations consistently favor encryption over password-only protection. Many tools follow guidance aligned with NIST encryption standards to ensure data remains protected against modern attack techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is password protection the same as encryption?
No. Password protection often controls access, while encryption protects the data itself.
Can a password-protected file be cracked?
In many cases, yes—especially with older formats or weak implementations.
Does encryption always require a password?
Not necessarily. Passwords are often used only to unlock encryption keys.
Why do some tools still offer password protection?
It is simpler and more familiar, but significantly less secure.
Should businesses rely on password protection?
No. Businesses should use proper file encryption to meet security and compliance needs.