Remote work has permanently changed how organizations handle files, access systems, and share information. In 2026, employees routinely work from home networks, personal devices, and public connections—often outside traditional security perimeters. File Encryption for Remote Work Security is no longer a niche concern; it is a core requirement for protecting company data wherever work happens.
This article explains how file encryption fits into remote work environments, what threats it actually mitigates, and where organizations commonly fail. Instead of focusing on tools or products, the emphasis is on workflows, key control, and realistic risk management. Understanding these factors helps organizations protect remote files without breaking productivity or pushing employees toward insecure workarounds.
Quick Navigation
Why Remote Work Increases File Security Risks
Untrusted Networks and Locations
Remote employees often use home Wi-Fi, shared networks, or public hotspots.
Personal and Mixed-Use Devices
Files may be accessed on devices that are not fully managed by IT teams.
Increased File Sharing
Remote work relies heavily on email, cloud platforms, and collaboration tools.
These risks are part of the broader context discussed in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide)
What File Encryption Protects in Remote Work
Files Outside the Office Network
Encryption keeps files protected even when accessed from untrusted environments.
Data on Lost or Stolen Devices
Encrypted files remain unreadable if laptops or external drives are lost.
Accidental File Exposure
Encryption reduces damage when files are mistakenly shared or synced.
A foundational explanation is covered in What Is File Encryption and Decryption?
Common Remote Work Threats Encryption Addresses
Unauthorized File Access
Encryption blocks access when files are copied or intercepted.
Insider Risk in Distributed Teams
Encryption limits exposure by enforcing access rules.
Cloud Account Compromise
Encrypted files remain unreadable even if cloud accounts are breached.
These threats are often underestimated and tied to poor practices outlined in Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid.
File Encryption Workflows for Remote Employees
Encrypting Files at Creation
Files should be encrypted automatically as soon as they are created or modified.
Decrypting Only When Necessary
Decryption should be temporary and limited to active use.
Avoiding Local Plaintext Copies
Encrypted workflows reduce the number of unprotected file copies.
A beginner-friendly process overview is available in How File Encryption Works (Beginner Friendly).
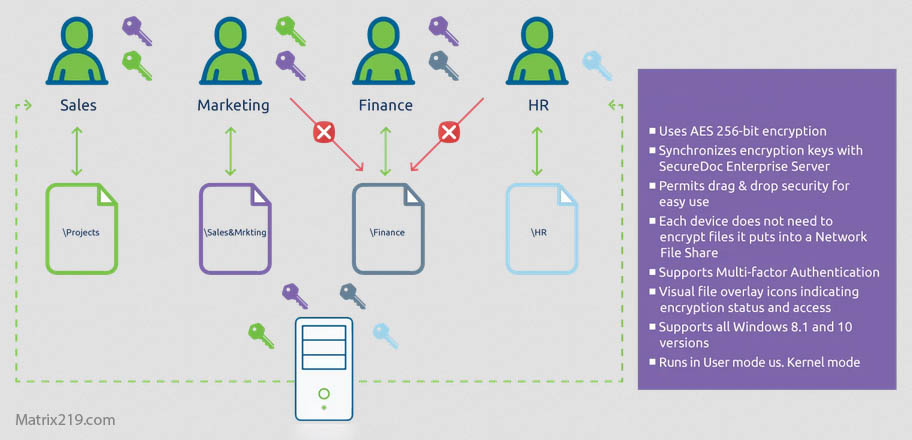
Key Management Challenges in Remote Environments
Distributing Keys Securely
Remote teams need secure methods for key exchange without email or chat exposure.
Revoking Access Quickly
Access must be removed immediately when roles change or devices are compromised.
Preventing Key Sprawl
Poor key handling increases long-term risk in distributed teams.
Key architecture principles are grounded in Symmetric vs Asymmetric File Encryption.
File Encryption and Cloud-Based Remote Work
Client-Side Encryption for Remote Teams
Encrypting files before cloud upload ensures consistent protection.
Syncing Across Multiple Devices
Keys must be securely available only to authorized endpoints.
Collaboration Trade-Offs
Stronger encryption may limit real-time editing features.
Cloud-specific workflows are discussed in File Encryption for Cloud Storage.
Performance and Usability in Remote Work
Minimizing Friction for Employees
Encryption should not add unnecessary steps to daily tasks.
Handling Large Files Remotely
Efficient encryption prevents slow uploads and downloads.
Avoiding Insecure Shortcuts
Overly complex encryption encourages users to bypass security.
Performance trade-offs are often misunderstood and discussed in Is File Encryption Really Secure?
When File Encryption Alone Is Not Enough
Compromised Endpoints
Encryption cannot protect files actively being used on infected devices.
Weak Remote Access Controls
Encryption must be combined with authentication and monitoring.
Lack of Security Awareness
Human behavior remains the largest risk factor.
These limitations reinforce the need for layered security.
How Businesses Should Implement Remote File Encryption
Define Remote Data Policies
Clear rules determine which files must always be encrypted.
Automate Encryption Where Possible
Automation reduces human error in remote workflows.
Plan for Incident Response
Key revocation and recovery must be documented in advance.
Business-focused planning is covered in File Encryption Software for Business
File Encryption Software for Business
Compliance Considerations for Remote Work
Data Protection Across Jurisdictions
Remote teams may access data from different legal regions.
Auditability and Access Records
Organizations must track access to encrypted files remotely.
Key Custody and Legal Accountability
Control of encryption keys often determines compliance outcomes.
Evaluations commonly align with NIST encryption standards when assessing remote encryption practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is file encryption mandatory for remote work?
In many organizations, yes—especially for sensitive or regulated data.
Does encryption slow down remote workflows?
Not when implemented correctly with modern tools.
Can encrypted files be shared remotely?
Yes, but encryption keys must be exchanged securely.
Is VPN enough without file encryption?
No. VPNs protect connections, not files themselves.
Should remote workers manage their own keys?
No. Organizations should retain key control whenever possible.





