Businesses face a very different risk landscape than individual users. In 2026, data breaches, insider threats, regulatory fines, and ransomware attacks make file protection a core business requirement—not an optional security add-on. File Encryption Software for Business is searched by organizations that need more than basic file locking. They need consistent protection, visibility, and control across teams, devices, and workflows.
This article explains what business-grade file encryption really means, how it differs from personal encryption tools, and which security capabilities are essential for companies of any size. Rather than focusing on specific vendors, the emphasis is on architecture, risk management, and operational reality. Understanding these fundamentals helps businesses avoid overpaying for unnecessary complexity—or worse, underprotecting sensitive data.
Quick Navigation
Why Businesses Need Dedicated File Encryption Software
Business Data Has Higher Consequences
Financial records, contracts, customer data, and intellectual property carry legal and financial risk if exposed.
Files Move Across Many Environments
Business files travel between employees, cloud platforms, partners, and external devices daily.
Compliance Is No Longer Optional
Many regulations explicitly require encryption for sensitive data at rest and in transit.
This broader context is explained in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide).
How Business File Encryption Differs From Personal Tools
Centralized vs Individual Control
Business encryption must be manageable centrally, not tied to a single user’s device or password.
Policy Enforcement
Organizations need consistent encryption rules applied automatically, not manually.
Auditability and Accountability
Businesses must be able to prove who accessed encrypted files and when.
These differences often determine whether a tool is suitable for professional use.
Core Features Required in Business File Encryption Software
Centralized Key Management
Encryption keys should be controlled, rotated, and revoked by policy, not stored individually by users.
Role-Based Access Control
Different users require different levels of access to encrypted files.
Secure File Sharing
Encrypted files must be shareable internally and externally without exposing keys.
Key architecture concepts are grounded in Symmetric vs Asymmetric File Encryption.
File Encryption for Teams and Collaboration
Shared Access Without Key Exposure
Business tools allow collaboration without distributing raw encryption keys.
Revoking Access Without Re-Encrypting Everything
Access should be removable instantly when employees leave or roles change.
Cross-Platform Support
Teams often use mixed operating systems, requiring consistent encryption behavior.
These collaboration challenges are not addressed by most free tools.
Business Encryption and Cloud Storage
Encrypting Files Before Cloud Upload
Businesses should retain control over encryption keys, even when using cloud platforms.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
Client-side encryption ensures cloud providers cannot access file contents.
Managing Cloud Access at Scale
Encryption must integrate with identity and access management systems.
Cloud-specific risks are discussed in File Encryption for Cloud Storage.
Performance and Scalability in Business Environments
Encrypting Large Volumes of Data
Business tools must handle bulk encryption without disrupting operations.
Minimizing Workflow Disruption
Encryption should be invisible to users whenever possible.
Hardware Acceleration and Optimization
Enterprise tools leverage modern hardware to reduce performance overhead.
Performance trade-offs are often misunderstood and linked to user behavior rather than encryption itself.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Encryption Requirements in Regulations
Many data protection laws require encryption as a baseline control.
Audit Logs and Reporting
Businesses must demonstrate compliance through documented access records.
Key Custody and Legal Responsibility
Who controls the keys often determines legal accountability.
Regulatory expectations are evaluated against NIST encryption standards in many compliance frameworks.
Common Business Encryption Mistakes
Treating Business Data Like Personal Files
Using consumer tools for business data increases risk dramatically.
Poor Offboarding Processes
Failing to revoke access leaves encrypted data exposed.
Overcomplicating Encryption Too Early
Complex systems without clear processes often fail operationally.
These errors are frequently detailed in Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid.
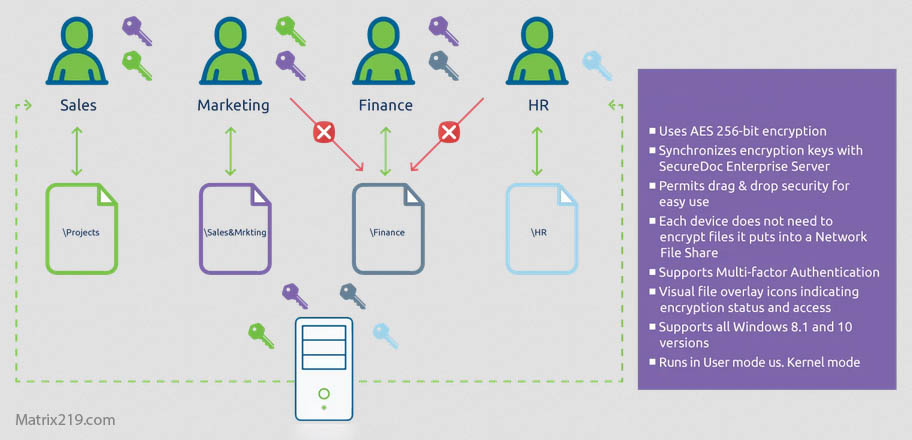
File Encryption Software for Business
When Businesses Should Avoid Free Encryption Tools
Lack of Central Management
Free tools cannot enforce organization-wide policies.
No Recovery or Escrow Options
Key loss can halt business operations permanently.
No Compliance Support
Free tools rarely provide audit or reporting capabilities.
A broader comparison is covered in Free vs Paid File Encryption Software.
How to Choose File Encryption Software for Business
Define Your Risk Model
Understand what data must be protected and from whom.
Match Encryption to Business Size
Small teams and enterprises require different levels of control.
Plan for Growth and Change
Encryption systems must scale with data volume and team size.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Do small businesses really need file encryption?
Yes. Smaller businesses are often targeted because they lack protection.
Is file encryption required for compliance?
In many cases, yes—especially for sensitive or regulated data.
Can business encryption slow down operations?
Not when implemented correctly with modern tools.
Who should control encryption keys in a company?
The organization—not individual employees—should retain key control.
Are business encryption tools difficult to manage?
Modern solutions are designed to reduce complexity through automation.





