Many users rely on file encryption with the assumption that once a file is encrypted, it is completely safe. Is File Encryption Really Secure? is a valid and necessary question in 2026, especially as data breaches continue to happen even in environments where encryption is supposedly in place. Encryption is a powerful security mechanism, but it is not a magic shield that eliminates all risks.
This article examines file encryption from a realistic security perspective. You will learn what encryption actually protects against, where its limits are, and why encrypted files are still compromised in real-world incidents. Understanding these boundaries is essential for anyone who wants to use encryption responsibly—without overestimating its guarantees or underestimating the role of human and operational factors.
Quick Navigation
What File Encryption Protects Against
Unauthorized File Access
Encryption prevents attackers from reading file contents if they obtain a copy without the correct key.
Physical Device Theft
Encrypted files remain protected even if storage devices are stolen or lost.
Accidental Data Exposure
Encryption reduces damage when files are mistakenly shared or uploaded.
A foundational explanation of how this protection works is covered in What Is File Encryption and Decryption?
What File Encryption Does NOT Protect Against
Compromised Devices
If malware runs on a device while files are decrypted, encryption offers no protection at that moment.
Legitimate Access Abuse
Encryption cannot stop authorized users from misusing or leaking decrypted data.
Poor Key Management
Lost, stolen, or weak keys instantly neutralize encryption security.
These risks are frequently underestimated and discussed in Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid.
Why Encrypted Files Still Get Breached
Human Error Is the Weakest Link
Most encryption failures are caused by users storing keys insecurely or reusing passwords.
Misconfigured Software
Incorrect settings may leave temporary files or backups unencrypted.
Trusting the Wrong Tools
Some software claims encryption but uses weak or incomplete implementations.
Warning signs are detailed in Signs Your File Encryption Software Is Fake.
The Role of Encryption Algorithms in Real Security
Strong Algorithms vs Weak Usage
Modern algorithms are mathematically secure, but security collapses when keys are mishandled.
Algorithm Choice Is Only One Layer
File encryption depends equally on key storage, access control, and operational discipline.
A technical overview of algorithms is available in Common File Encryption Algorithms (AES, RSA, ChaCha20).
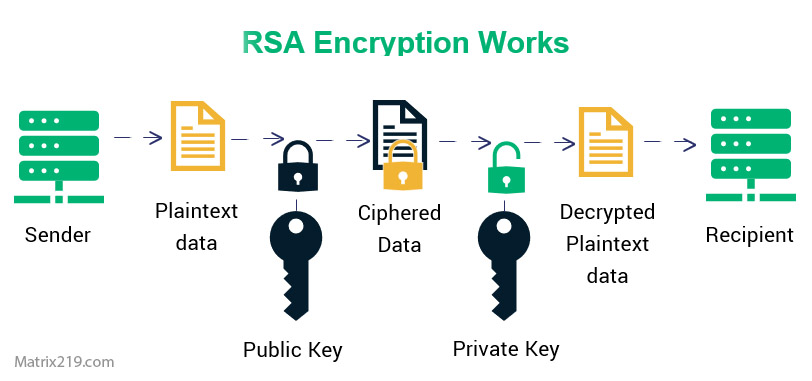
RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography
Encryption and Performance Trade-Offs
Why Some Users Disable Encryption
Performance slowdowns lead some users to weaken or bypass encryption.
Balancing Security and Usability
Well-designed tools minimize overhead while maintaining protection.
Performance-related risks are often misunderstood and tied to user behavior rather than encryption itself.
File Encryption in Shared and Cloud Environments
Encryption During File Sharing
Encrypted files remain secure, but key exchange introduces new risks.
Cloud Storage Realities
Encryption is effective only when applied before files are uploaded.
These scenarios are explored further in File Encryption for Cloud Storage.
When File Encryption Is Considered “Secure Enough”
Low-Risk Personal Data
For personal files, encryption significantly reduces exposure.
Business and Regulated Data
Encryption is required but must be combined with policies, auditing, and recovery planning.
A broader security framework is explained in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide).
How Security Standards View File Encryption
Security frameworks treat encryption as a critical control, not a standalone solution. Many assessments align with NIST encryption standards to evaluate whether encryption remains effective under real operational conditions.
How to Use File Encryption Securely in Practice
Control Your Encryption Keys
Keys should never be stored alongside encrypted files.
Encrypt Before Sharing or Uploading
Always encrypt files before they leave your local environment.
Plan for Failure Scenarios
Backup strategies must include secure key recovery plans.
Recovery risks are discussed in What Happens If You Lose an Encryption Key?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is file encryption completely secure?
No. It is highly effective, but not immune to poor practices or compromised systems.
Can encrypted files be hacked?
Not directly, but weak keys or exposed devices can lead to access.
Does encryption stop ransomware?
It can limit damage but does not prevent infection.
Is encryption enough for businesses?
No. It must be combined with access control and monitoring.
Should all files be encrypted?
Only files that carry risk or sensitivity should be encrypted.