Lock SIM & carrier actions after phone hacking are often overlooked—but they’re critical. Even if you secure your email and accounts, a compromised SIM card can let attackers intercept verification codes, reset passwords, or hijack your number through SIM swap attacks. In many real incidents, the phone isn’t the weakest link—the SIM is.
This article explains when SIM-related actions are necessary, what to do with your carrier, and how to lock down your number without causing service disruptions. If attackers touched your accounts or you received unexplained SMS codes, this step should not be skipped.
Quick Navigation
Why the SIM Card Is a High-Value Target
Attackers don’t always need your phone.
What control over your SIM enables
-
Intercepting SMS-based verification codes
-
Resetting accounts tied to your number
-
Performing SIM swap fraud with carrier support
If your number is compromised, account recovery becomes unstable.
For the full incident overview, review: If Your Phone Is Hacked: How to Know, What to Do, and How to Stay Safe
When You Should Take SIM and Carrier Action
Not every case requires carrier escalation—but many do.
Strong indicators SIM action is needed
-
You stop receiving calls or texts unexpectedly
-
Verification codes arrive that you didn’t request
-
Your phone shows “No Service” intermittently
-
Accounts reset using SMS despite password changes
If these appear, SIM security becomes urgent.
For immediate-response sequencing, see: What to do immediately if your phone is hacked
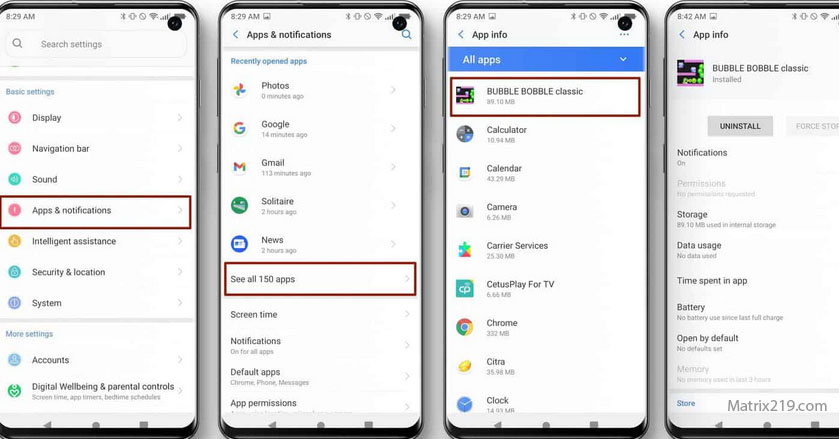
If Your Phone Is Hacked Step-by-Step Recovery Guide Android & iPhone
Step 1: Set or Change Your SIM PIN
This is the fastest protective step.
Why SIM PIN matters
-
Prevents SIM use in another device
-
Blocks basic SIM swap attempts
-
Adds a physical security layer
Set a strong PIN and avoid obvious numbers. Store it offline.
Step 2: Contact Your Mobile Carrier
Carrier-side protection closes common attack paths.
What to ask your carrier to do
-
Flag your account for potential fraud
-
Add a port-out PIN or account password
-
Review recent SIM changes or requests
If SIM swap is suspected, request a new SIM with the same number and invalidate the old one.
For cases where account compromise already occurred, follow the recovery order here: If Your Phone Is Hacked: Step-by-Step Recovery Guide (Android & iPhone)
Step 3: Reduce Dependence on SMS Verification
SMS is convenient—but weaker.
Safer alternatives to switch to
-
Authenticator apps
-
Hardware security keys (where supported)
-
App-based confirmations
If SMS remains your only option, SIM security becomes non-negotiable.
Related guidance: Change passwords first or reset phone
Step 4: Monitor for Ongoing SIM Abuse
Assume nothing—verify behavior.
Warning signs after SIM lockdown
-
Delayed or missing texts
-
Repeated carrier notifications
-
Account alerts tied to phone number
If any appear, re-contact your carrier and pause high-risk activity.
How SIM Security Fits Into Full Recovery
SIM action supports—but does not replace—other steps.
What SIM protection does well
-
Blocks number-based takeovers
-
Prevents easy account resets via SMS
What it does not fix
-
Email compromise
-
Cloud account access
-
Spyware on the device
For safe access removal across layers, review: Remove hacker access safely
Consumer protection advisories consistently warn that SIM swap attacks are a primary method used to bypass two-step verification, which is why carrier-level locks and port-out PINs are recommended after any suspected account or phone compromise SIM swap fraud prevention guidance
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to change my phone number after hacking?
Not usually—locking the SIM and carrier account is often enough.
Is SIM PIN the same as phone lock PIN?
No. SIM PIN protects the card itself, not the device.
Can attackers bypass a SIM PIN?
It greatly raises the barrier, especially combined with carrier locks.
Should I switch all accounts away from SMS?
Yes, where possible—especially email and financial accounts.
What if my carrier is uncooperative?
Escalate to fraud support and document all interactions.