Choosing between different encryption models is one of the most misunderstood parts of file security. Symmetric vs Asymmetric File Encryption is not a debate about which method is “better,” but about how each model solves a specific problem in protecting files. In 2026, most users interact with both types daily—often without realizing it—when encrypting files locally, sharing them securely, or collaborating across networks.
This article explains the real differences between symmetric and asymmetric file encryption in practical terms. You will learn how each model works, where it excels, where it falls short, and why modern file encryption software rarely relies on only one of them. Understanding this distinction is essential for evaluating encryption tools realistically and avoiding security assumptions that break down in real-world use.
Quick Navigation
What Symmetric File Encryption Is
One Key for Encryption and Decryption
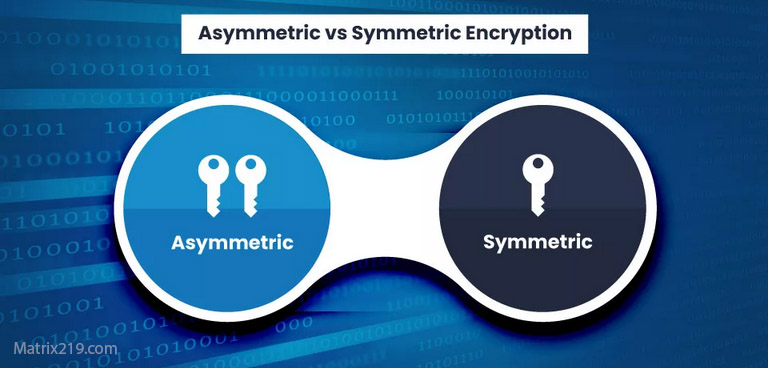
Symmetric encryption uses a single secret key to both encrypt and decrypt files. Anyone with that key can access the data.
Why Symmetric Encryption Is Fast
Because it relies on simpler mathematical operations, symmetric encryption is highly efficient, even for very large files.
Common Symmetric Use Cases
This model is widely used for local file protection, backups, and bulk data encryption.
A conceptual overview is available in What Is File Encryption and Decryption?
What Asymmetric File Encryption Is
Two Keys Working Together
Asymmetric encryption uses a public key to encrypt files and a private key to decrypt them. The private key is never shared.
Why Asymmetric Encryption Is Slower
The mathematics behind asymmetric encryption are more complex, making it less efficient for large files.
Where Asymmetric Encryption Is Essential
It is ideal for secure key exchange and identity-based access rather than bulk file encryption.
Core Differences Between Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption
Key Management Complexity
Symmetric encryption requires secure key sharing, while asymmetric encryption reduces this risk by separating public and private keys.
Performance and Scalability
Symmetric encryption scales well for large data volumes, while asymmetric encryption scales better for multi-user environments.
Security Assumptions
Asymmetric encryption assumes private keys remain protected, while symmetric encryption assumes keys are shared securely.
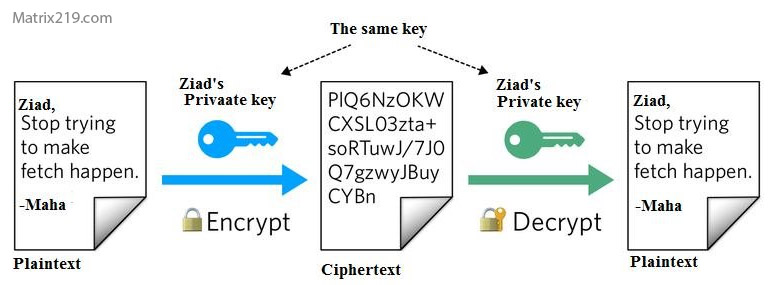
How File Encryption Works
Why Most File Encryption Software Uses Both
Hybrid Encryption Models Explained
Modern file encryption tools encrypt files symmetrically, then protect the symmetric key using asymmetric encryption.
Benefits of the Hybrid Approach
This combination provides both speed and secure key distribution without sacrificing usability.
Where Hybrid Models Appear in Practice
Hybrid encryption is standard in secure file sharing, cloud encryption, and enterprise environments.
This architecture is discussed further in How File Encryption Works (Beginner Friendly).
Real-World Scenarios and Model Selection
Local File Encryption
Symmetric encryption is usually sufficient and more efficient.
Secure File Sharing
Asymmetric encryption enables safe key exchange between users who do not share secrets in advance.
Business and Team Environments
Hybrid models support access control, auditing, and scalability.
Related use cases are explored in File Encryption Software for Business.
Common Misunderstandings About Encryption Models
“Asymmetric Encryption Is Always More Secure”
Security depends on correct implementation and key handling, not just the model.
“Symmetric Encryption Is Outdated”
Symmetric algorithms remain foundational to modern encryption systems.
“One Model Is Enough”
Relying on a single model often creates usability or security gaps.
These misconceptions frequently appear in Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid.
How Standards Evaluate Encryption Models
Security standards do not favor one model universally. Instead, they define appropriate use cases for each. Many modern tools follow guidance aligned with NIST encryption standards to ensure symmetric and asymmetric algorithms are applied correctly within secure systems.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Needs
Ask Practical Questions
-
Are files shared with others?
-
Is performance critical?
-
How are keys stored and exchanged?
Match the Model to the Workflow
Local protection favors symmetric encryption, while collaboration favors asymmetric or hybrid systems.
A full decision framework is provided in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is symmetric encryption less secure than asymmetric encryption?
No. It is highly secure when keys are generated and stored properly.
Why not encrypt files directly with asymmetric encryption?
It is inefficient for large files and increases processing overhead.
Do users need to manage both types manually?
No. Modern software handles hybrid encryption automatically.
Can asymmetric encryption replace passwords?
It can reduce reliance on passwords but does not eliminate access control needs.
Which model is better for cloud file encryption?
Hybrid encryption is typically the most practical and secure option.