Understanding how files are protected is no longer optional in a world where data constantly moves between devices, cloud platforms, and external storage. What Is File Encryption and Decryption? is a question many users ask when they want to protect documents but feel overwhelmed by technical explanations. At its core, file encryption is about transforming readable data into an unreadable format so that only authorized users can access it, while decryption is the controlled process of restoring that data to its original form.
This article explains these concepts in clear, practical terms—without marketing hype or unnecessary complexity. You will learn why file-level encryption matters, how it differs from other protection methods, and what risks appear when encryption is misunderstood or misused. This foundation is critical before choosing any tool or software, especially if you plan to rely on encryption daily for personal, professional, or business-critical files.
Quick Navigation
File Encryption Explained in Simple Terms
What Happens When a File Is Encrypted
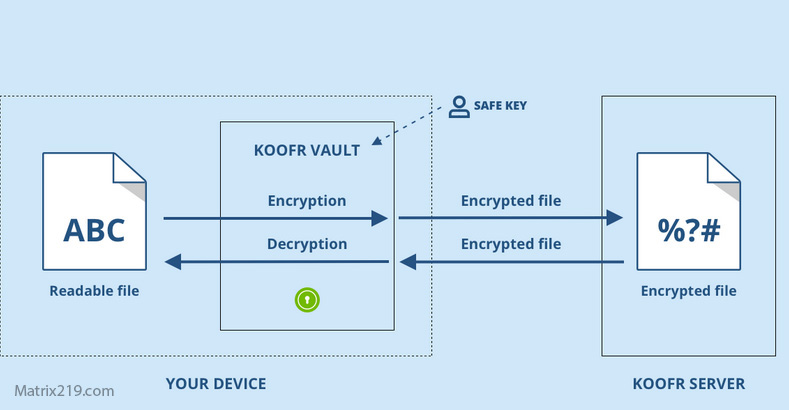
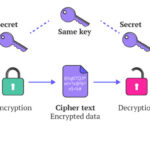
When you encrypt a file, its contents are mathematically transformed using an algorithm and a secret key. The result is a file that looks like random data to anyone without the correct key.
Why Encrypted Files Are Unreadable
Without the key, the encrypted file cannot be interpreted, even if someone copies or steals it. This is what separates encryption from simple file hiding.
What Is File Decryption?
Controlled Restoration of Data
Decryption reverses the encryption process using the correct key or credentials, restoring the file to its original usable state.
Why Decryption Must Be Secure
Poorly designed tools may expose data temporarily during decryption, increasing the risk of leaks or malware interception.
File Encryption vs Other File Protection Methods
Encryption vs Password Protection
Password-protected files may only restrict access at the application level, while encryption protects the file itself.
Encryption vs File Obfuscation
Obfuscation hides data visually but does not prevent reconstruction, unlike true encryption.
A deeper comparison is available in Encryption vs Password Protection.
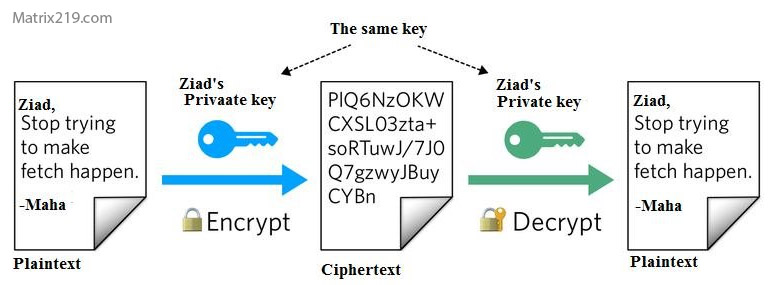
How File Encryption Works
File Encryption vs Disk Encryption
Scope of Protection
File encryption protects individual files wherever they go, while disk encryption protects data only while it remains on a specific device.
Why File-Level Encryption Matters
Once files are shared or uploaded, disk encryption no longer applies.
This distinction is explained further in File Encryption vs Disk Encryption.
Core Components of File Encryption Systems
Encryption Algorithms
Algorithms define how data is transformed. Strong algorithms are public, tested, and widely reviewed.
Encryption Keys
Keys control access. Losing a key often means permanent data loss.
Access Control Logic
Good software enforces who can decrypt files and under which conditions.
These fundamentals are explored in Common File Encryption Algorithms (AES, RSA, ChaCha20).
Common Use Cases for File Encryption
Personal File Protection
Encrypting personal documents prevents exposure if devices are lost or stolen.
Professional and Business Scenarios
Businesses rely on encryption to protect contracts, financial records, and sensitive communications.
Practical examples are discussed in File Encryption Software for Business.
Why File Encryption Can Fail
Weak Passwords and Key Handling
Encryption is only as strong as the key protecting it.
Misconfigured Software
Incorrect settings can expose files despite encryption.
False Sense of Security
Using the wrong tool may lead users to believe files are protected when they are not.
Related risks are detailed in Common File Encryption Mistakes to Avoid.
How File Encryption Fits Into a Larger Security Strategy
Encryption Is Not a Standalone Solution
It must be combined with backups, access control, and secure workflows.
Planning for Key Loss and Recovery
Users should decide in advance how keys are stored and backed up.
Recovery scenarios are discussed in What Happens If You Lose an Encryption Key?
When You Should Learn More Before Choosing Software
Understanding file encryption concepts helps you evaluate tools realistically and avoid overpaying for features you do not need—or underprotecting sensitive data. A complete framework for choosing tools is covered in Best File Encryption and Decryption Software in 2026 (Complete Guide) and supported by standards such as NIST encryption standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is file encryption difficult to use?
Modern tools simplify encryption, but understanding the basics prevents costly mistakes.
Can encrypted files be opened on any device?
Only if the software and key are compatible across systems.
Does encryption change the file permanently?
No. The original file can be restored through decryption if the key is available.
Is file encryption legal?
Yes, and often required for protecting sensitive data.
Can encryption stop all data breaches?
It reduces risk significantly but cannot prevent breaches caused by poor practices.