How Websites Track You is a question that often comes up when users notice ads following them across different sites or content changing based on previous activity. In reality, most tracking happens silently, using technologies that work behind the scenes without requiring user interaction or explicit approval in many cases.
Websites do not rely on a single tracking method. Instead, they combine multiple techniques to recognize visitors, measure behavior, and build usage profiles over time. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for anyone who wants to reduce unnecessary data exposure and make informed decisions about online privacy.
This article explains the main technologies websites use to track users, how they work together, and why they are difficult to avoid completely.
Quick Navigation
Why Websites Track Users
Website tracking serves several purposes beyond advertising. Site owners use tracking to understand visitor behavior, improve performance, detect fraud, and personalize content. For many platforms, tracking data directly supports business models and operational decisions.
Because of this, tracking is deeply integrated into modern web infrastructure rather than being an optional add-on.
Cookies and Browser Storage
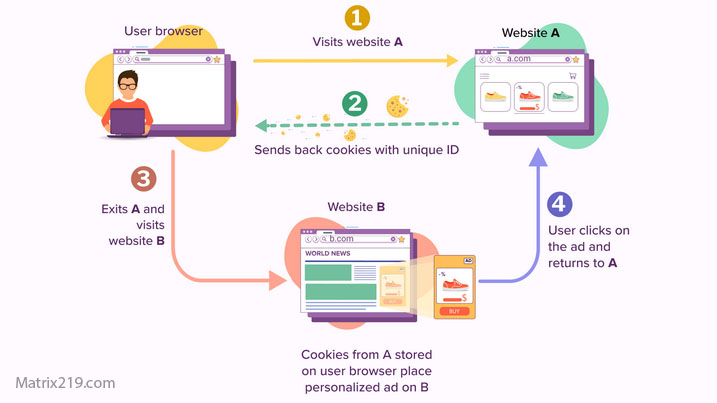
Cookies are one of the most widely known tracking tools. They store small pieces of data in the browser that help websites recognize returning users and remember preferences.
While some cookies are necessary for functionality, others are designed for analytics or advertising. In addition to cookies, browsers also store data using local storage and session storage, which can persist even when cookies are cleared.
Third-Party Trackers
Many websites load content from external domains. These third parties can place their own tracking technologies on user devices, allowing them to monitor activity across multiple sites.
This is how advertising networks and analytics providers build cross-site profiles. Even if you trust a website, its embedded third-party services may still collect data independently.
To see how this fits into the larger privacy picture, review: Digital Privacy and Online Tracking: How You’re Tracked Online and How to Protect Yourself
Browser Fingerprinting Techniques
Browser fingerprinting identifies users by analyzing technical characteristics instead of storing data. Factors such as device type, operating system, browser version, installed fonts, and time zone all contribute to a unique fingerprint.
Because fingerprinting does not rely on stored identifiers, it is harder to block using traditional privacy tools.
A deeper explanation of this method is available here: Browser Fingerprinting Explained
How Websites Track You
Session Replay and Behavioral Tracking
Some websites use session replay tools to record how users interact with pages. These tools can capture mouse movements, scrolling behavior, and form interactions.
While often used for usability testing, session replay can raise privacy concerns if sensitive information is collected or stored improperly.
Account-Based Website Tracking
When users are logged into accounts, tracking becomes directly linked to identity. Activity across different websites owned by the same company can be combined into a single profile.
This allows platforms to understand user behavior beyond individual sessions or devices, significantly expanding tracking capabilities.
Why Blocking Website Tracking Is Difficult
Blocking one tracking method does not stop others. Clearing cookies may remove stored identifiers, but fingerprinting and account-based tracking can still identify users.
Effective privacy protection requires understanding how these layers interact rather than relying on a single solution.
For practical steps to reduce exposure, see: How to Stop Online Tracking
The Impact of Website Tracking on Users
Website tracking affects what content users see, which ads appear, and how platforms prioritize information. Over time, this can influence opinions, choices, and access to opportunities.
Awareness of tracking mechanisms allows users to make better decisions about which sites to trust and how to interact with them.
FAQ
How do websites track users without login?
Websites use cookies, browser storage, fingerprinting, and third-party trackers to recognize users even without account login.
Can clearing cookies stop website tracking?
Clearing cookies removes some identifiers, but other methods like fingerprinting can still track users.
Are all website trackers harmful?
Not all tracking is malicious. Some is necessary for functionality and security, but excessive tracking increases privacy risks.
Do privacy browsers stop website tracking?
Privacy-focused browsers reduce tracking significantly, but they cannot eliminate all tracking methods.
Is website tracking legal?
Tracking legality depends on region and implementation. Many laws require disclosure, but they do not prohibit tracking entirely.




